HTTP
Topics in this section,
In this section, you are going to learn
HTTP
terminology
# |
Version |
|---|---|
Ubuntu |
Ubuntu 22.04 64 bit |
Linux Kernel |
6.5.0 |
High Level Protocol Setup
Experimental Setup
Command |
Version |
Dependent Libraries |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
pwd |
coreutils 8.32 |
|
Prints the current working directory. |
apt |
2.4.13 (amd64) |
|
Command-line interface for package management in Debian-based systems like Ubuntu.Provides easy access to installation,removal,and management of software packages. |
squid |
5.9 |
|
The squid command starts the Squid proxy server,which acts as a caching proxy to optimize web traffic.It supports protocols like HTTP,HTTPS,and FTP,helping reduce bandwidth usage,improve response times, and control access to internet resources. |
systemctl |
systemd 249 |
|
It is used to control and manage systemd services and the system state on Linux.It allows you to start, stop, restart,enable, disable, and check the status of services and system units. |
netstat |
net-tools 2.10-alpha |
|
It provides detailed information about network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, and network protocol usage on a computer or server. It is commonly used for network troubleshooting, monitoring, and diagnosing network-related issues. |
curl |
7.81.0 |
|
curl (short for Client URL) is a command-line tool and library used for transferring data with URLs. It supports a wide range of protocols, such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS,SCP, SFTP, SMTP, IMAP, and more. It’s commonly used for interacting with web services, testing APIs, and fetching data over the internet.It can be used to send requests to servers and retrieve responses, upload files, or interact with APIs for tasks such as authentication, file downloads, and much more. |
wget |
1.21.2 |
|
wget is a command-line utility for downloading files from the web. It supports HTTP, HTTPS,and FTP protocols, and allows non-interactive downloads, resuming interrupted downloads,and recursive downloading of websites. It’s commonly used for automating file transfers and mirroring websites. |
telnet |
0.17-44build1 |
|
It is used to connect to remote systems over a network for testing and remote communication though it lacks encryption and is less secure than SSH. |
ping |
iputils 20211215 |
|
It is used to check if a computer or server is reachable over a network. It sends a small packet of data to the target and waits for a reply. If it gets a response, it means the target is online and reachable. |
Library |
Path |
Version |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
linux-vdso.so.1 |
(virtual DSO - no path, provided by kernel) |
N/A |
Virtual dynamic shared object for system calls optimization (provided by kernel) |
libc.so.6 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 |
2.35 |
GNU C Library — core system functionality like memory allocation, I/O, etc. |
ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 |
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 |
2.35 |
Dynamic linker/loader — prepares and runs dynamic executables |
libapt-private.so.0.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libapt-private.so.0.0 |
2.4.13 |
Internal library used by APT tools (Advanced Package Tool). |
libapt-pkg.so.6.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libapt-pkg.so.6.0 |
2.4.13 |
Core library of APT, handling package management and retrieval. |
libstdc++.so.6 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6 |
12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 |
Standard C++ library for handling C++ programs and features. |
libgcc_s.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcc_s.so.1 |
12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 |
GCC low-level runtime library for exception handling. |
libz.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libz.so.1 |
1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2 |
Zlib compression library for file compression and decompression. |
libbz2.so.1.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libbz2.so.1.0 |
1.0.8-5build1 |
Bzip2 compression library. |
liblzma.so.5 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/liblzma.so.5 |
5.2.5-2ubuntu1 |
XZ compression library. |
liblz4.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/liblz4.so.1 |
1.9.3-2build2 |
LZ4 compression library. |
libzstd.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libzstd.so.1 |
1.4.8+dfsg-3build1 |
Zstandard compression library, for fast compression. |
libudev.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libudev.so.1 |
249.11-0ubuntu3.12 |
Library for interacting with the udev device manager. |
libsystemd.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsystemd.so.0 |
249.11-0ubuntu3.12 |
Systemd library for managing system services. |
libgcrypt.so.20 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcrypt.so.20 |
1.9.4-3ubuntu3 |
Library for cryptographic algorithms. |
libxxhash.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libxxhash.so.0 |
0.8.1-1 |
Library for fast, non-cryptographic hash function (XXHash). |
libm.so.6 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libm.so.6 |
2.35-0ubuntu3.9 |
Math library providing common mathematical functions. |
ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 |
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 |
2.35-0ubuntu3.9 |
The dynamic linker for ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) binaries. |
libcap.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcap.so.2 |
1:2.44-1ubuntu0.22.04.2 |
Library for handling POSIX capabilities. |
libgpg-error.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgpg-error.so.0 |
1.43-3 |
Library for handling errors related to GnuPG (Gnu Privacy Guard). |
libnettle.so.8 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnettle.so.8 |
3.7.3-1build2 |
Cryptographic library providing low-level cryptographic primitives. |
libecap.so.3 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libecap.so.3 |
1.0.1-3.2ubuntu4 |
eCAP – content adaptation framework. |
libxml2.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libxml2.so.2 |
2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.6 |
XML parsing library |
libexpat.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libexpat.so.1 |
2.4.7-1ubuntu0.6 |
XML parser library written in C |
libgnutls.so.30 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgnutls.so.30 |
3.7.3-4ubuntu1.6 |
TLS and SSL protocols implementation |
libgssapi_krb5.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgssapi_krb5.so.2 |
1.19.2-2ubuntu0.6 |
Kerberos 5 GSS-API library. |
libkrb5.so.3 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libkrb5.so.3 |
1.19.2-2ubuntu0.6 |
Core Kerberos library. |
libcom_err.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcom_err.so.2 |
1.46.5-2ubuntu1.2 |
Common error description library. |
libsystemd.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsystemd.so.0 |
249.11-0ubuntu3.12 |
System and service manager. |
libcap.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcap.so.2 |
1:2.44-1ubuntu0.22.04.2 |
POSIX capabilities library |
libnetfilter_conntrack.so.3 |
|
1.0.9-1 |
Netfilter connection tracking library. |
libltdl.so.7 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libltdl.so.7 |
2.4.6-15build2 |
Libtool dynamic module loader |
libicuuc.so.70 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libicuuc.so.70 |
70.1-2 |
Unicode support library. |
libp11-kit.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libp11-kit.so.0 |
0.24.0-6build1 |
PKCS#11 proxy library. |
libidn2.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libidn2.so.0 |
2.3.2-2build1 |
Internationalized Domain Names library. |
libunistring.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libunistring.so.2 |
1.0-1 |
Unicode string manipulation. |
libtasn1.so.6 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtasn1.so.6 |
4.18.0-4ubuntu0.1 |
ASN.1 parser library. |
libhogweed.so.6 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libhogweed.so.6 |
3.7.3-1build2 |
Cryptographic library (used with Nettle). |
libgmp.so.10 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so.10 |
2:6.2.1+dfsg-3ubuntu1 |
Arithmetic on big numbers. |
ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 |
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 |
2.35-0ubuntu3.9 |
Loads and links programs |
libk5crypto.so.3 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libk5crypto.so.3 |
1.19.2-2ubuntu0.6 |
Kerberos cryptographic library |
libkrb5support.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libkrb5support.so.0 |
1.19.2-2ubuntu0.6 |
Support routines for Kerberos. |
libkeyutils.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libkeyutils.so.1 |
1.6.1-2ubuntu3 |
Key management utilities. |
libresolv.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libresolv.so.2 |
2.35-0ubuntu3.9 |
DNS resolver library. |
libnfnetlink.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnfnetlink.so.0 |
1.0.1-3build3 |
Netfilter communication library |
libmnl.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libmnl.so.0 |
1.0.4-3build2 |
Minimalistic Netlink library |
libicudata.so.70 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libicudata.so.70 |
70.1-2 |
International Components for Unicode. |
libffi.so.8 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libffi.so.8 |
3.4.2-4 |
Foreign Function Interface library |
libselinux.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libselinux.so.1 |
3.3-1build2 |
SELinux security policies support. |
libblkid.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libblkid.so.1 |
2.37.2-4ubuntu3.4 |
Identifies block devices (partitions, file systems, etc.). |
libpcre2-8.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpcre2-8.so.0 |
10.39-3ubuntu0.1 |
Perl-compatible regular expression engine (PCRE2). |
libcurl.so.4 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcurl.so.4 |
7.81.0-1ubuntu1.20 |
Client-side URL transfer library supporting various protocols like HTTP, FTP, and more |
libnghttp2.so.14 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnghttp2.so.14 |
1.43.0-1ubuntu0.2 |
HTTP/2 C library implementing RFC 7540. |
libidn2.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libidn2.so.0 |
2.3.2-2build1 |
Internationalized domain name (IDN) library. |
librtmp.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/librtmp.so.1 |
2.4+20151223. gitfa8646d.1-2build4 |
RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) client library. |
libssh.so.4 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libssh.so.4 |
0.9.6-2ubuntu0.22.04.3 |
SSH (Secure Shell) protocol library. |
libpsl.so.5 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpsl.so.5 |
0.21.0-1.2build2 |
Public Suffix List library for domain name parsing. |
libssl.so.3 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libssl.so.3 |
3.0.2-0ubuntu1.19 |
OpenSSL SSL/TLS cryptographic library. |
libldap-2.5.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libldap-2.5.so.0 |
2.5.18+dfsg- 0ubuntu0.22.04.3 |
OpenLDAP libraries for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) servers and clients. |
liblber-2.5.so.0 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/liblber-2.5.so.0 |
2.5.18+dfsg-0ubuntu 0.22.04.3 |
OpenLDAP libraries for BER (Basic Encoding Rules) encoding/decoding. |
libbrotlidec.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libbrotlidec.so.1 |
1.0.9-2build6 |
Brotli decompression library. |
libsasl2.so.2 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsasl2.so.2 |
2.1.27+dfsg2-3ubuntu1.2 |
Cyrus SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) library. |
libbrotlicommon.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libbrotlicommon.so.1 |
1.0.9-2build6 |
Brotli compression common library. |
libtasn1.so.6 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtasn1.so.6 |
4.18.0-4ubuntu0.1 |
ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax Notation One) library. |
libuuid.so.1 |
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libuuid.so.1 |
2.37.2-4ubuntu3.4 |
Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) library |
Step-1 : Find the IP address of Ubuntu machine
test:~$ ifconfig docker0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 172.17.0.1 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.17.255.255 ether 02:42:c2:a4:22:08 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet) RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 enp0s31f6: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 10.91.239.121 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.91.239.255 inet6 fe80::bb87:2721:82b8:f6cd prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether e4:54:e8:4e:e4:b9 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 10426884 bytes 7818062595 (7.8 GB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 3605750 bytes 434038103 (434.0 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 device interrupt 16 memory 0xdf000000-df020000 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 1097677 bytes 88297298 (88.2 MB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 1097677 bytes 88297298 (88.2 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0Note
To find the IP address of your Ubuntu machine,use the ifconfig command.
From the output of ifconfig command,for example, 10.91.239.121 is used as the Proxy Server IP.
This Proxy server IP is used when connecting HTTP server to a client.
Step-2 : Install Squid Proxy Server on Ubuntu
test:~$ pwd /home/test test:~$ sudo apt update test:~$ sudo apt install squidStep-3 : Verify the Installation
test:~$ squid -vStep-4 : Edit the Squid Configuration file
test:~$ sudo nano /etc/squid/squid.conf #specify the port for squid to listen http_port 3128 #Define an ACL for the client (replace with your client's IP) acl client_ip src 192.168.0.10 #this could be the actual IP of the client #Allow the client IP to access the proxy http_acess allow client_ip acl safe_ports port 80 #Allow access to safe ports(which is just HTTP in this case) http_access allow safe_ports #Deny all other clients from accessing the proxy http_access deny all #Logging and cache settings (optional) access_log /var/log/squid/access.log cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 #default cache directory with 100MB space visible_hostname sysadmin //optional #Persistent Connection Handling client_persistent_connections off server_persistent_connections off .. note:: comment all the lines in file the above prompt only to save.
Step-5 : Start the Squid server
test:~$ sudo systemctl restart squid test:~$ sudo systemctl enable squid test:~$ sudo systemctl status squid
Note
If server is not running,check logs at “sudo journalctl -u squid” or “sudo systemctl status squid” and fix the errors.
Step-6 : Allow connection from port 3128 (http port)
test:~$ sudo ufw allow 3128
Step-7 : To check the server is listening on port
test:~$ sudo netstat -tuln | grep 3128 tcp6 0 0 :::3128 :::* LISTEN
Step-8 : To view the logs
test:~$ sudo tail -f /var/log/squid/access.log
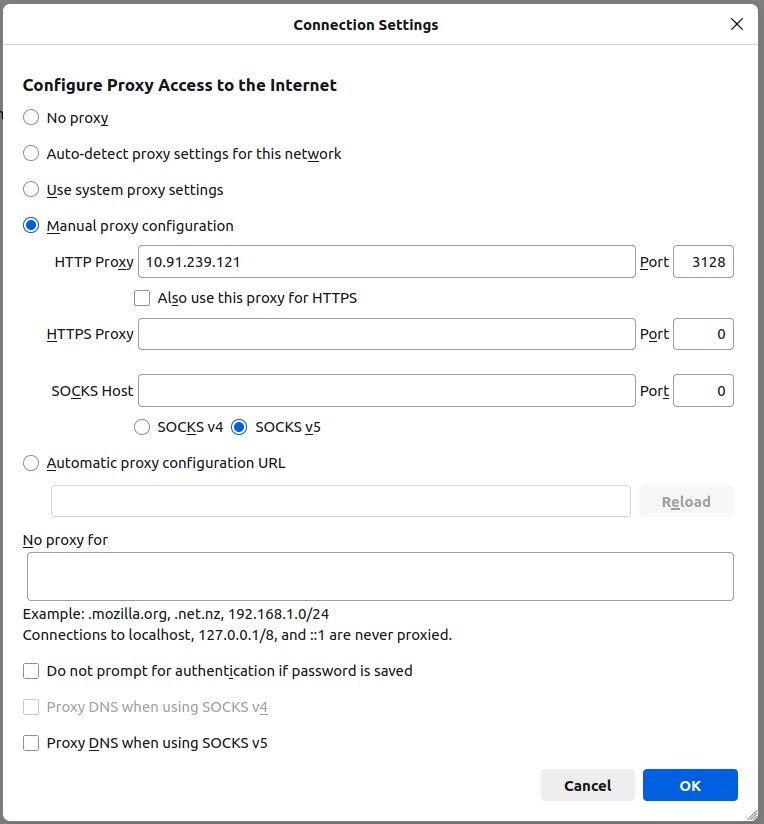
- 1.Open firefox preferences.
Open firefox on your machine.
In the top-right corner,click on the three horizontal lines(the hamburger menu).
Click on settings.
- 2.Access Proxy settings
Scroll down to the Network Settings Section.
Click the settings button next to Network Settings.
- 3.Configure the Proxy
A new window will appear with various options to configure the Proxy settings.
Select Manual Proxy Configuration.
HTTP Proxy: Enter the IP address of your proxy server (e.g., 10.91.239.121).
Port: Enter the Port number (e.g., 3128,the default squid port).
Click OK.
Then restart the firefox.
4.Then search on firefox,it loads the webpages in browser.
5.Check on terminal also
test:~$ firefox http://www.example.com
It loads the webpage in browser.
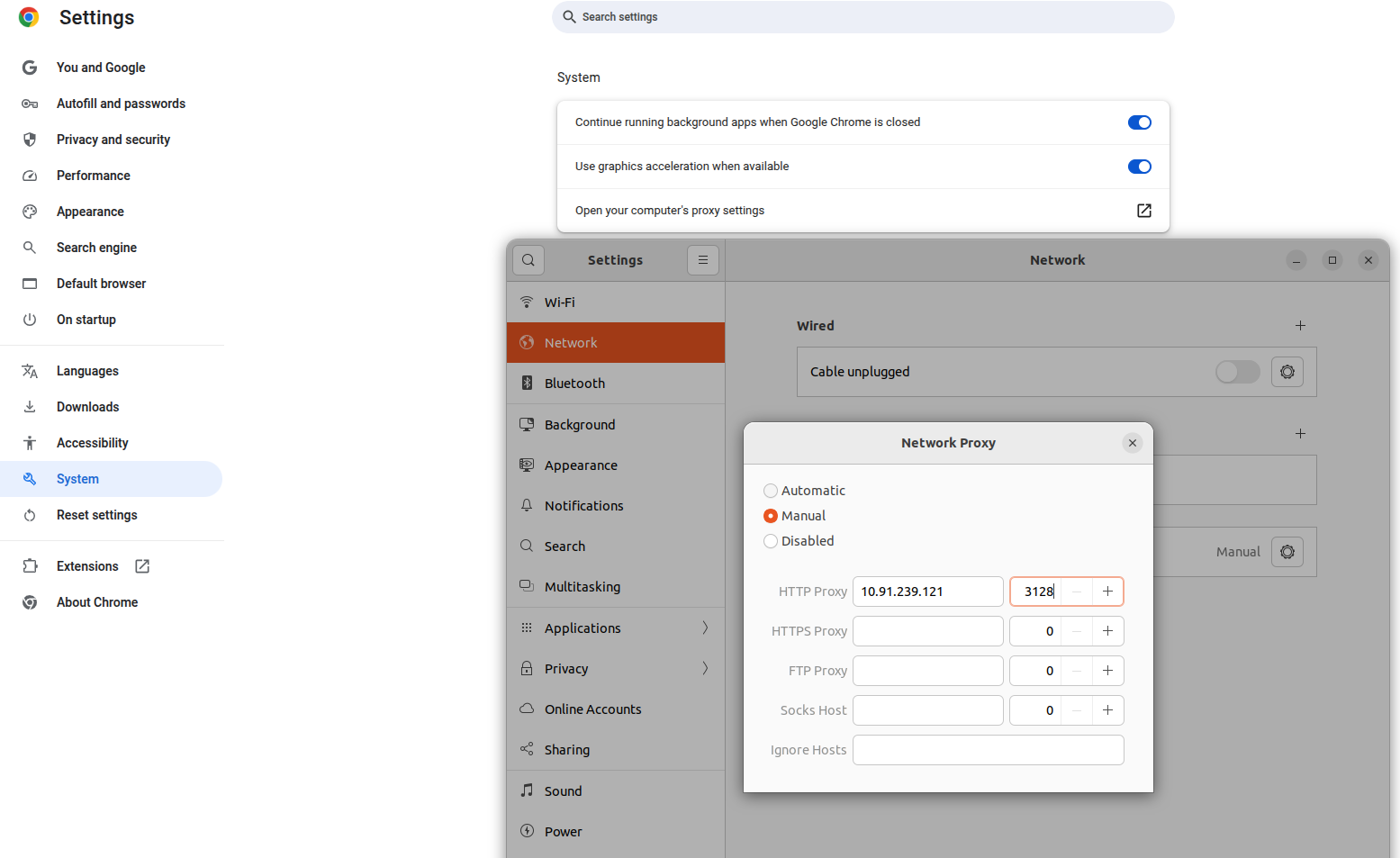
- 1.Open chrome on your machine.
In the top-right corner,click on the three dots.
click on settings.
2.Scroll down to the system in that click on open your computer proxy settings.
3.In that proxy tab to click the NetworkProxy ON and below the configuration select manual option.
4.And enter Proxy server’s IP address and port number in the HTTP Proxy.
5.After that open the chrome and search http://google.com.
6.If the Proxy is setup correctly,it loads the webpages.
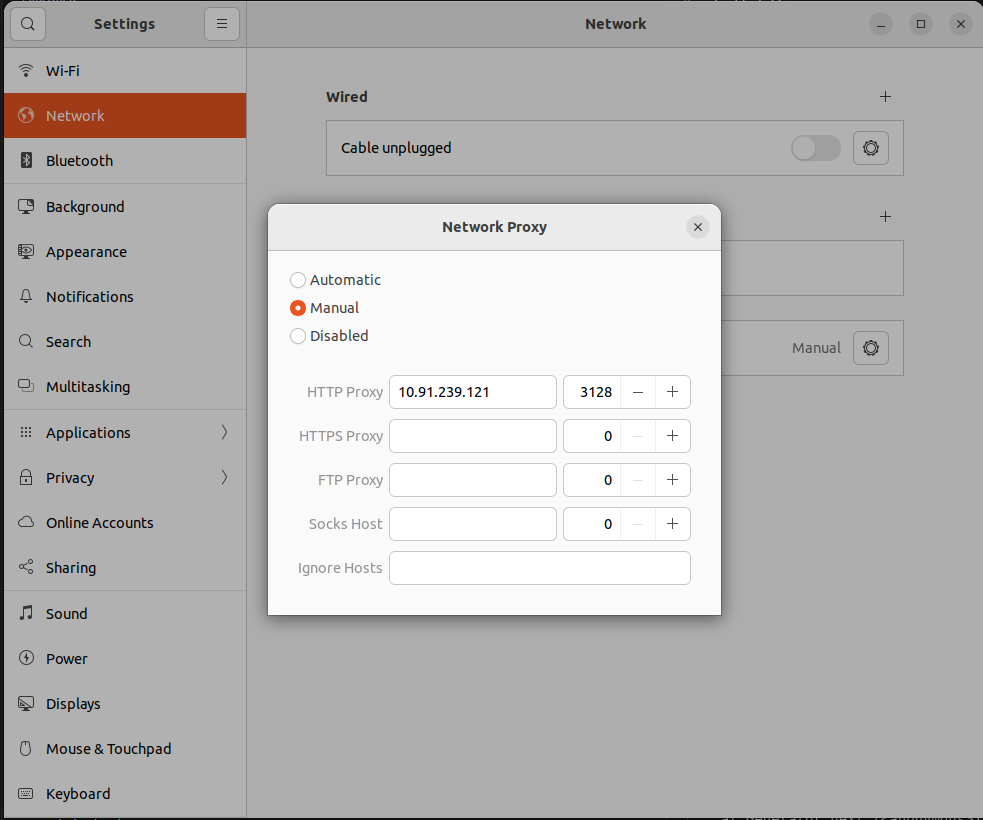
1.Click on the top-right corner of the screen.
2.Click on the settings in that select Network Proxy and click the option Manual.
3.And enter Proxy server’s IP address and port number in the HTTP Proxy.
4.If the proxy is setup correctly,check on firefox or chrome and serach like http://google.com.
Step-1 : Using Telnet
test:~$ telnet 10.91.239.121 3128 Trying 10.91.239.121... Connected to 10.91.239.121. Escape Character is '^]'.
If the connection fails,the output will be something like connection refused or unable to connect.
Note
10.91.239.121 is the Proxy Server IP address referenced in the “Setup HTTP Proxy Server on Ubuntu” section above.
Step-2 : Using netcat
test:~$ nc -zv 10.91.239.121 3128 Connection to 10.91.239.121 3128 port [tcp/* ] succeeded!
Note
10.91.239.121 is the Proxy Server IP address referenced in the “Setup HTTP Proxy Server on Ubuntu” section above.
Step-3 : Using ping
test:~$ ping 10.91.239.121 PING 10.91.239.13 (10.91.239.121 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.91.239.121: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.092 ms 64 bytes from 10.91.239.121: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms 64 bytes from 10.91.239.121: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.094 ms 64 bytes from 10.91.239.121: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.105 ms 64 bytes from 10.91.239.121: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.094 ms
Note
10.91.239.121 is the Proxy Server IP address referenced in the “Setup HTTP Proxy Server on Ubuntu” section above.
test:~$ curl --proxy http://10.91.239.121:3128 http://www.google.com
Expected output:The HTML source code of the webpage hosted at http://www.google.com
Note
10.91.239.121 is the Proxy Server IP address referenced in the “Setup HTTP Proxy Server on Ubuntu” section above.
Step-1 : wireshark captures
client side
server side
Step-2 : Analysis of Client side Wireshark Capture
- 1.TCP Three-Way Handshake Connection - SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK
Packet 1:SYN - client(192.168.0.10) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 2:SYN-ACK - client(192.168.0.10) <- proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 3:ACK - client(192.168.0.10) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)

- 2.HTTP Request and Response and TCP Data Transfer
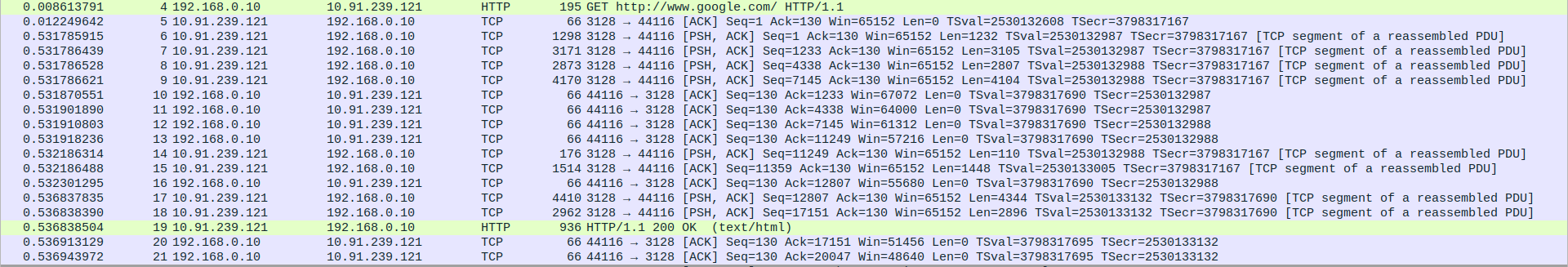
Packet 4: HTTP GET request from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy(10.91.239.121) for http://www.google.com/.
Packet 5: TCP ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (192.168.0.10).
Packets 6-9: TCP segments (PSH, ACK) from prox (10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10), transmitting large chunks of data.
Packets 10-13: TCP ACKs from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy(10.91.239.121) acknowledging data chunks.
Packet 14: TCP segment (PSH, ACK) with additional data from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packet 15: TCP ACK with more data from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packet 16: TCP ACK from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy (10.91.239.121).
Packets 17-18: Additional TCP data from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packet 19: HTTP 200 OK response from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packets 20-21: Final TCP ACKs from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy(10.91.239.121).
- 3.TCP Connection Termination - FIN-ACK,ACK
Packet 22:FIN-ACK - client(192.168.0.10) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 23:ACK - client(192.168.0.10) <- proxyserver(10.91.239.121)

Step-3 : Analysis of Server side Wireshark Capture
- 2.HTTP Request and Acknowledgment
Packet 14: The client (10.91.239.123) sends an HTTP GET request to the proxy(10.91.239.121) for http://www.google.com/.
Packet 15: The proxyserver(10.91.239.121) acknowledges receipt of the HTTP request with a TCP ACK (no data, just acknowledgment).

- 3.TCP Three-Way Handshake Connection between Proxyserver and webserver - SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK
Packet 16:SYN - proxyserver(10.91.239.121) -> webserver(142.250.196.164)
Packet 17:SYN-ACK - proxyserver(10.91.239.121) <- webserver(142.250.196.164)
Packet 18:ACK - proxyserver(10.91.239.121) -> webserver(142.250.196.164)

- 4.HTTP Communication Between Proxy and Web Server(Google)
- 1.HTTP GET Request from Proxy to Google
Packet 19: Proxy sends GET / HTTP/1.1 to Google (142.250.196.164), initiating an HTTP request.
- 2.TCP Acknowledgment and Response Begins
Packet 20: Google acknowledges the request (ACK for Seq 202).
Packet 23: Google sends the first 1400 bytes of the HTTP response data (part of the content).
Packet 24: Proxy acknowledges receiving these 1400 bytes.
- 3.Proxy Forwards Data to Client
Packet 25: Proxy starts forwarding the received data to the client (10.91.239.123) via port 3128.
- 4.Continuation of HTTP Response from Google
Packets 26–27: Google sends the next 2800 bytes in two segments of 1400 bytes each.
Packets 28–29: Proxy sends ACKs for those segments.
Packet 30: Proxy forwards more data (3105 bytes) to the client.
- 5.More Response Segments from Google
Packets 31–32: Google sends additional 2800 bytes (2 × 1400 bytes).
Packets 33–34: Proxy acknowledges them.
Packet 35: Proxy forwards 2807 bytes more to the client.
- 6.Larger Response Blocks and Final Transfer
Packets 36–37: Google sends another 4200 bytes in two packets.
Packets 38–39: Proxy acknowledges these.
Packet 40: Proxy sends 4104 bytes more to client.
Packet 41: Google sends next 2800 bytes.
Packet 42: Proxy acknowledges.
- 7.Final HTTP Segments
Packet 43: Proxy sends final 110 bytes to the client.
Packet 44: Google continues with another 1400 bytes.
Packet 45: Proxy acknowledges.
Packets 46–47: Google sends 2800 bytes more.
Packets 48–49: Proxy sends ACKs.
Packet 50: Google sends 1400 bytes again.
Packet 51: Proxy acknowledges.
- 8.Final HTTP Response
Packet 52: Google sends the final HTTP response with status 200 OK and content (likely the full HTML of the page).
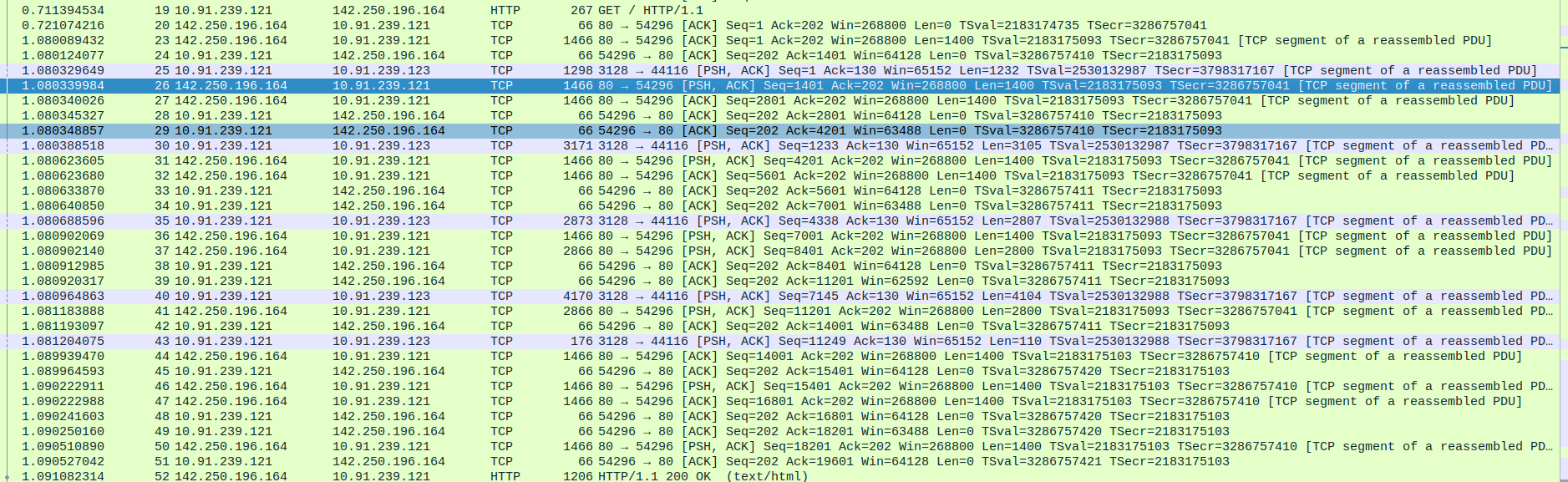
- 6.TCP Data Transfer Between Proxy server(10.91.239.121) and Client(10.91.239.123)
Packets 56–59: ACK packets from the proxy to the client, acknowledging the successful receipt of data.
Packet 60: ACK packet from the client to the proxy, confirming data receipt.
Packets 61–62: Data push (PSH, ACK) packets from the client to the proxy, sending data in chunks.
Packet 63: ACK packet from the proxy to the client, acknowledging the client’s data.
Packet 64: HTTP 200 OK response from the proxy to the client, delivering the requested content (webpage).
Packets 65–66: ACK packets from the proxy to the client, confirming the receipt of the last data.
test:~$ wget -e use_proxy=yes -e http_proxy=http://10.91.239.121:3128 http://www.google.com
Expected output:The HTML content of the webpage at http://www.google.com
Note
10.91.239.121 is the Proxy Server IP address referenced in the “Setup HTTP Proxy Server on Ubuntu” section above.
Step-1 : wireshark captures
client side
server side
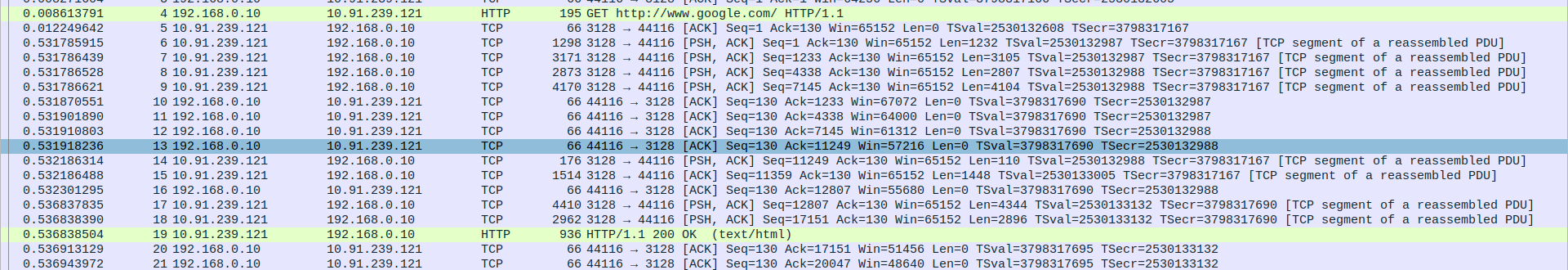
Step-2 : Analysis of Client side wireshark capture
- 1.TCP Three-Way Handshake Connection - SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK
Packet 1:SYN - client(192.168.0.10) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 2:SYN-ACK - client(192.168.0.10) <- proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 3:ACK - client(192.168.0.10) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)

- 2.HTTP Request and Response and TCP Data Transfer
Packet 4: HTTP GET request from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy(10.91.239.121) for http://www.google.com/.
Packet 5: TCP ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (192.168.0.10).
Packets 6-9: TCP segments (PSH, ACK) from prox (10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10), transmitting large chunks of data.
Packets 10-13: TCP ACKs from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy(10.91.239.121) acknowledging data chunks.
Packet 14: TCP segment (PSH, ACK) with additional data from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packet 15: TCP ACK with more data from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packet 16: TCP ACK from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy (10.91.239.121).
Packets 17-18: Additional TCP data from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packet 19: HTTP 200 OK response from proxy(10.91.239.121) to client(192.168.0.10).
Packets 20-21: Final TCP ACKs from client(192.168.0.10) to proxy(10.91.239.121).
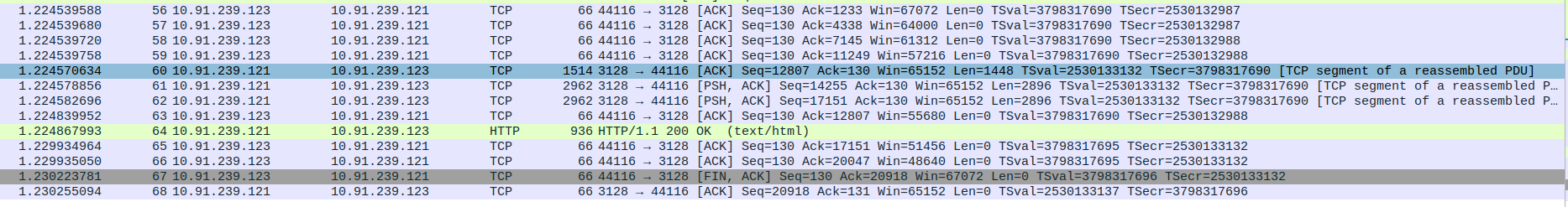
- 3.TCP Connection Termination - FIN-ACK,ACK
Packet 22:FIN-ACK - client(192.168.0.10) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 23:ACK - client(192.168.0.10) <- proxyserver(10.91.239.121)

Step-3 : Analysis of Server side wireshark capture
- 1.TCP Three-Way Handshake Connection - SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK
Packet 1:SYN - client(10.91.239.123) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 2:SYN-ACK - client(10.91.239.123) <- proxyserver(10.91.239.121)
Packet 3:ACK - client(10.91.239.123) -> proxyserver(10.91.239.121)

- 2.HTTP Request and Acknowledgment
Packet 4: The client (10.91.239.123) sends an HTTP GET request to the proxy(10.91.239.121) for http://www.google.com/.
Packet 5: The proxyserver(10.91.239.121) acknowledges receipt of the HTTP request with a TCP ACK (no data, just acknowledgment).
Packet 6: DNS query (A record) sent to resolve IPv4 address for www.google.com from server (10.91.239.121) to DNS server (216.239.34.10).
Packet 7: DNS query (AAAA record) sent to DNS server for the IPv6 address of www.google.com.
Packet 8: DNS response with IPv6 address (AAAA record) of www.google.com.
Packet 9: DNS response with IPv4 address (A record) of www.google.com (142.250.196.164).
Packet 10: DNSSEC query for domain verification of google.com sent to DNS server (192.42.93.30).
Packet 11: DNSSEC response from server, containing NSEC3, RRSIG, and SOA records, authenticating the domain.
Packet 12: TCP SYN sent to DNS server (192.42.93.30) to initiate a DNS over TCP connection.
Packet 13: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) message from a network switch, unrelated to the web traffic.
Packet 14: TCP SYN-ACK sent by the DNS server (192.42.93.30) in response to SYN from proxy.
Packet 15: TCP ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to confirm the connection establishment.
Packet 16: DS DNS query again sent by proxy over TCP for DNSSEC information for google.com.
Packet 17: DNSSEC response from server containing additional records for verification.
Packet 18: Browser Election Request sent on the local network by a client (10.91.239.109).
Packet 19: TCP ACK sent to confirm receipt of the DNSSEC response.
Packet 20: TCP FIN-ACK sent by the proxy to close the connection with the DNS server.
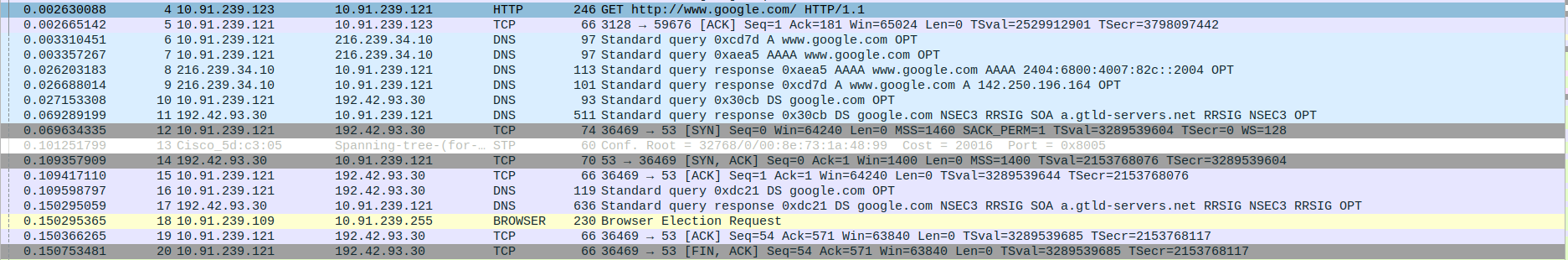
- 3.TCP Three-Way Handshake Connection between Proxyserver and webserver - SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK
Packet 21:SYN - proxyserver(10.91.239.121) -> webserver(142.250.196.164)
Packet 22:SYN-ACK - proxyserver(10.91.239.121) <- webserver(142.250.196.164)
Packet 23:ACK - proxyserver(10.91.239.121) -> webserver(142.250.196.164)

- 4.HTTP Request, DNS Query and Response, ICMP Echo Reply, and TCP Connection Termination between DNS Server and Proxy server
Packet 24:The client sends an ICMP Echo request (ping) to Google
Packet 25: The client sends an HTTP GET request to retrieve a page from Google.
Packet 26: Google server acknowledges the HTTP GET request.
Packet 27: Google server replies with an ICMP echo reply to the client’s ping request.
Packet 28: The DNS server sends a FIN-ACK to close the TCP connection after completing DNS resolution.
Packet 29: The client sends an ACK to confirm the connection termination with the DNS server.
- 5.HTTP Communication between proxy and webserver(Google)
Packet 30: ACK from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), TCP Seq=1, Ack=229.
Packet 31: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=1401.
Packet 32: Data from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), PSH, ACK, 2866 bytes.
Packet 33: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=4201.
Packet 34: Data from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (10.91.239.123), PSH, ACK, 1297 bytes.
Packet 35: Data from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (10.91.239.123), PSH, ACK, 3165 bytes.
Packet 36: ACK from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), TCP Seq=4201, Ack=229.
Packet 37: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=7001.
Packet 38: Data from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (10.91.239.123), PSH, ACK, 2873 bytes.
Packet 39: Data from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy(10.91.239.121), PSH, ACK, 1466 bytes.
Packet 40: ACK from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), TCP Seq=8401, Ack=229.
Packet 41: ACK from proxy(10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=9801.
Packet 42: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=10201.
Packet 43: Data from proxy (10.91.239.121) to device (10.91.239.123), PSH, ACK, 2873 bytes.
Packet 44: Data from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), PSH, ACK, 2866 bytes.
Packet 45: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=12601.
Packet 46: Data from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (10.91.239.123), PSH, ACK, 2873 bytes.
Packet 47: ACK from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), TCP Seq=12601, Ack=229.
Packet 48: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=14001.
Packet 49: Data from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), PSH, ACK, 1320 bytes.
Packet 50: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=15255.
Packet 51: Data from proxy (10.91.239.121) to client (10.91.239.123), ACK, 1514 bytes.
Packet 52: ACK from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), TCP Seq=15255, Ack=229.
Packet 53: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=16655.
Packet 54: Data from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), PSH, ACK, 2866 bytes.
Packet 55: ACK from proxy (10.91.239.121) to Google (142.250.196.164), TCP Seq=229, Ack=19455.
Packet 56: Data from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121), PSH, ACK, 1302 bytes.
Packet 57: HTTP 200 OK response from Google (142.250.196.164) to proxy (10.91.239.121).
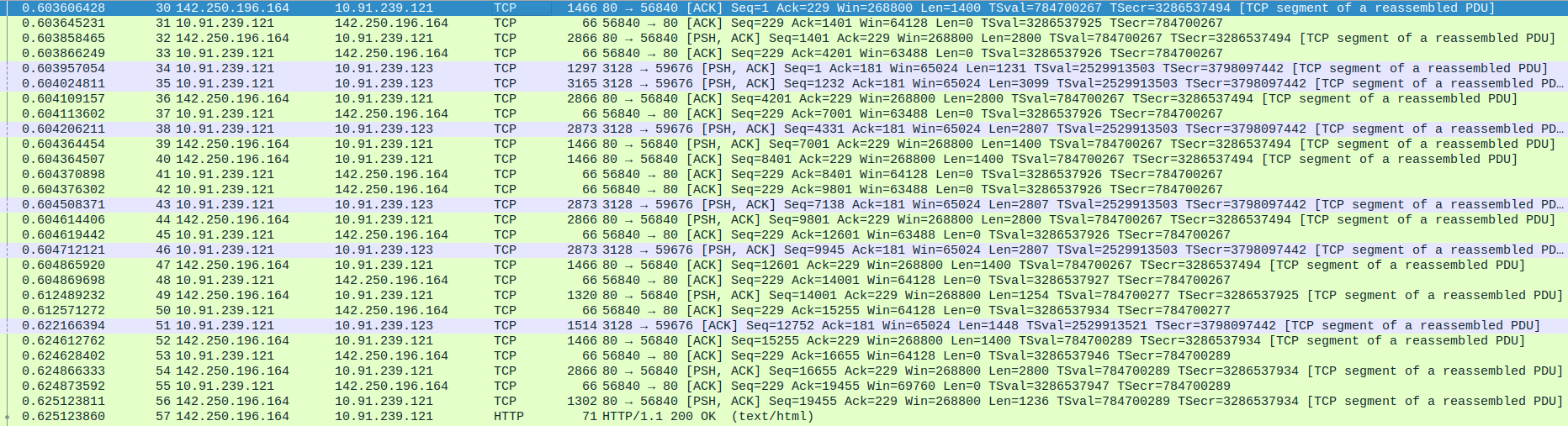
- 6.TCP Connection Termination between Proxy server and webserver(Google) - FIN-ACK,ACK
Packet 58:FIN-ACK - webserver(142.250.196.164) -> proxy(10.91.239.121)
Packet 59-60:ACK - proxy(10.91.239.121) -> webserver(142.250.196.164)
Packet 61:FIN-ACK - proxy(10.91.239.121) -> webserver(142.250.196.164)
Packet 62:ACK - webserver(142.250.196.164) -> proxy(10.91.239.121)

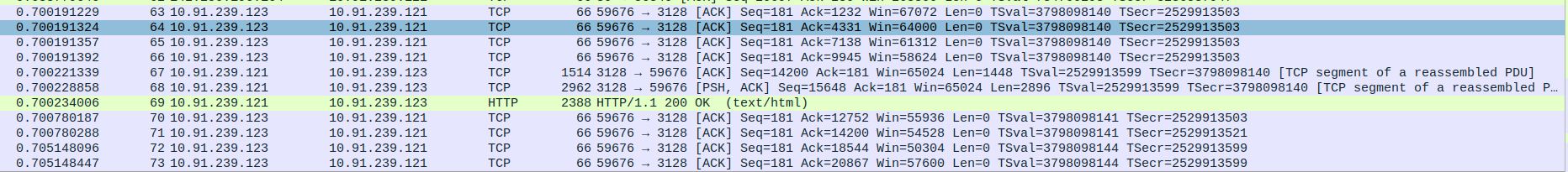
- 7.TCP Data Transfer Between Proxy server(10.91.239.121) and Client(10.91.239.123)
Packets 63–66: ACK packets from the proxy to the client, acknowledging the successful receipt of data in sequence.
Packet 67: ACK packet from the client to the proxy, acknowledging data receipt and sending additional data.
Packet 68: Data push (PSH, ACK) packet from the client to the proxy, sending a larger chunk of data.
Packet 69: HTTP 200 OK response from the proxy to the client, delivering the requested content (webpage).
Packets 70–71: ACK packets from the proxy to the client, confirming the receipt of data.
Packets 72–73: ACK packets from the proxy to the client, acknowledging further data receipt in the ongoing transaction.
FAQs
Reference links