Open-Wrt: Add shared library
What is Shared Library ?
How to create a shared library in Open-WRT ?
How to link shared library with object files for RPI-4B ?
How to flash full openwrt image for RPI-4B ?
How to run minicom and work remotely with RPI-4B ?
Topics in this section,
PART A: CREATING SHARED LIBRARY
Step 1: Add custom built library
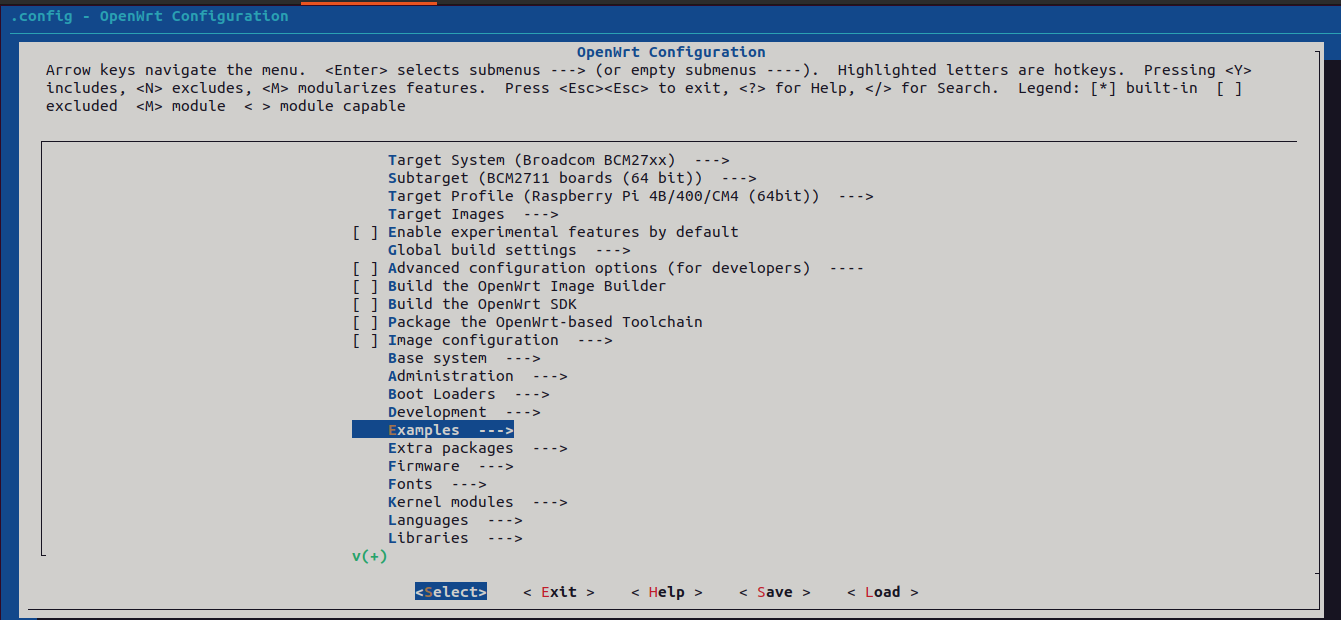
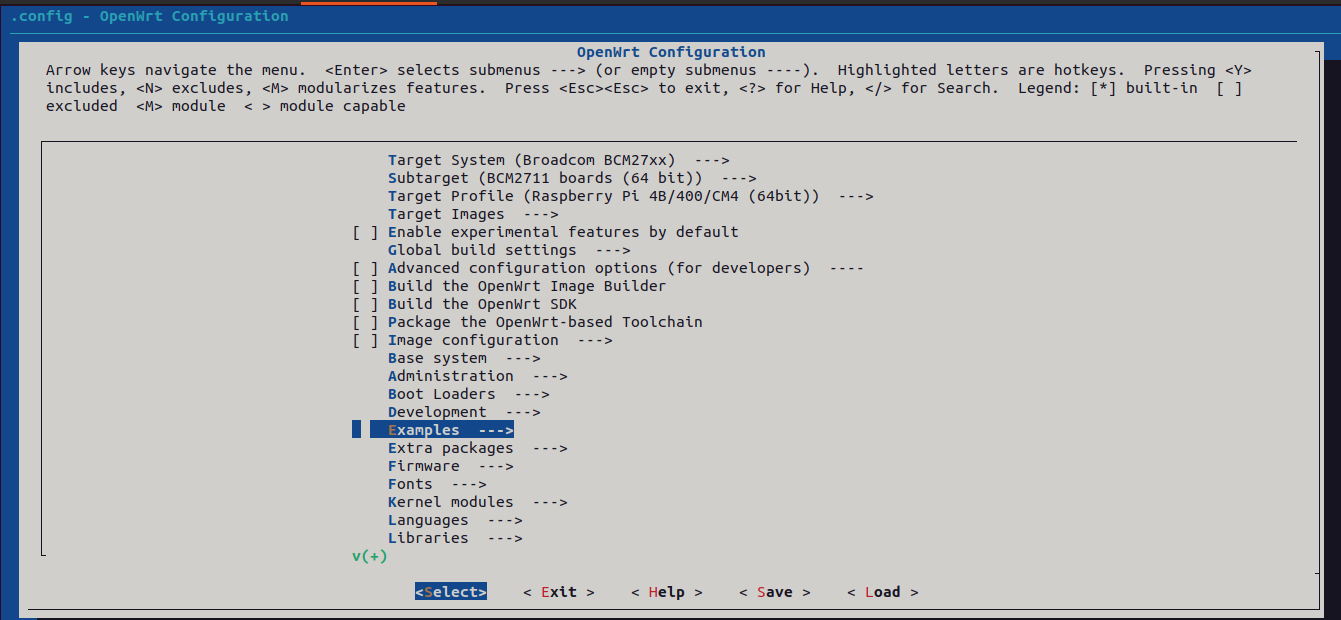
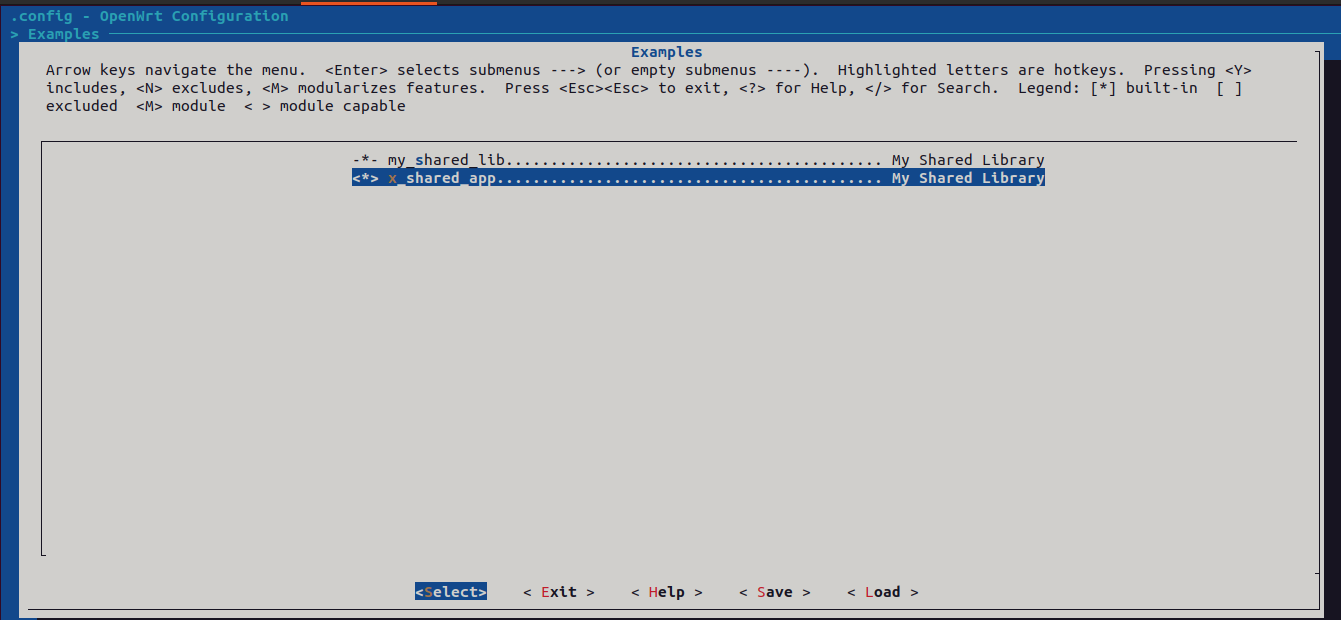
Step 2 : Add application package to menuconfig
Step 3 : Update and install feeds
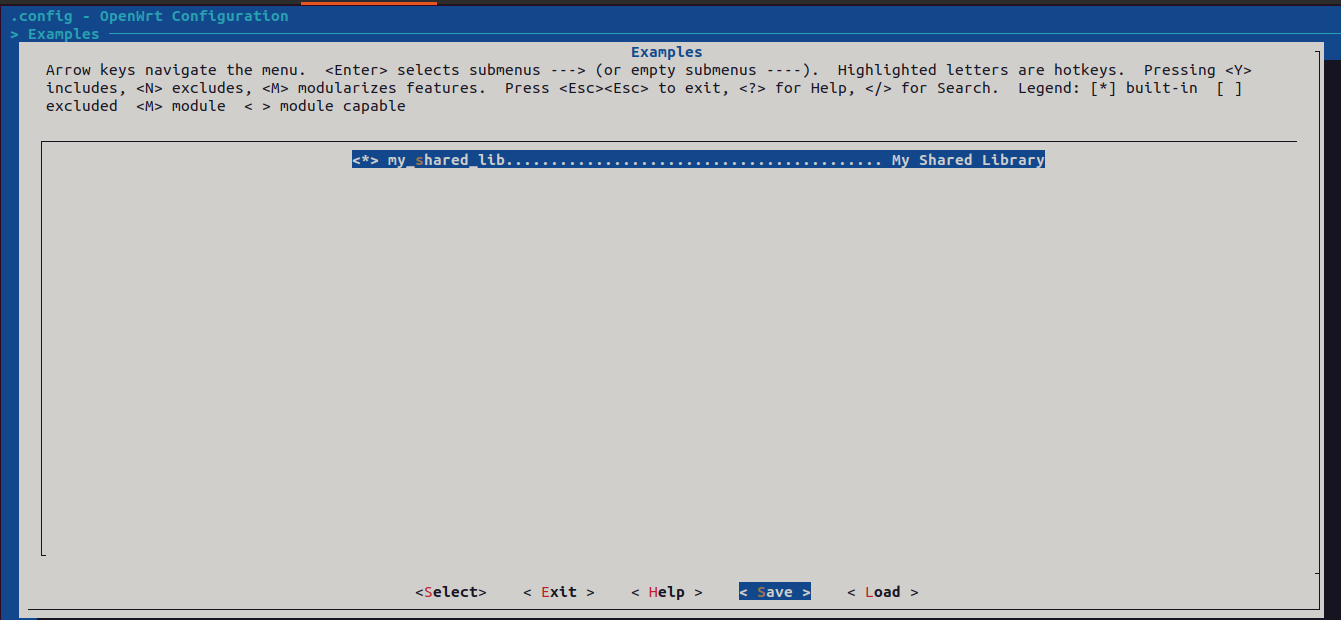
Step 4 : Enable application package in menuconfig
Step 7.2: Check the “objdump” output of the shared library file
Step 7.3: Check the “readelf” output of the shared library file
Step 7.5: Check the “file” command output of shared library (.so) file
Step 7.6: Check the “size” command output of shared library file
Step 7.7: Check the “strings” command output of shared library file
Step 8: Build full openwrt - Incremental
Topics in this section,
PART B: CREATING SHARED APPLICATION
Step 1 : Add custom built library
Step 2 : Add application package to menuconfig
Step 3 : Update and install feeds
Step 4 : Enable application package in menuconfig
Step 7.1 Check the location of the shared application binary file
Step 7.2: Check the “objdump” output of the shared application file
Step 7.3: Check the “readelf” output of the shared application file
Step 7.4: Check the “nm” output of the shared application file
Step 7.5: Check the “file” command output of shared application file
Step 7.6: Check the “size” command output of shared application file
Step 7.7: Check the “strings” command output of shared application file
Step 8: Build full openwrt - Incremental
Note
PART A: Creating Shared Library
Note
Create 2 folders in alphabet order so that library side makefile should execute first and it will create .so shared library file
In this section you will learn how to add custom built library in “Openwrt”
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$ pwd /home/test/openwrt
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$ cd package/libs/ $ mkdir -p shared_lib/my_shared_lib
Make sure the current directory “my_shared_lib”
$ cd my_shared_lib
Make sure the current directory “my_shared_lib/src”
In my_shared_lib.c have “Function Definition”
Create my_shared_lib.c file using vim command
vim my_shared_lib.c
Content of src/my_shared_lib.c
#include "my_shared_lib.h" void my_shared_function(void) { printf("Hello from my_shared_function!\n"); }
Make sure the current directory “my_shared_lib/inc”
In my_shared_lib.h have “Function Prototype”
Create my_shared_lib.h file using vim command
vim my_shared_lib.h
Content of inc/my_shared_lib.h
#include <stdio.h> void my_shared_function(void);What is Shared Library ?
See Answer
Collection of compiled object code that is linked to the source code only at the runtime.
What are the types of library ?
See Answer
- Two types of library:
Static Library
Shared Library
What is the use of library ?
See Answer
It is a collection of pre-compiled functions that can be used by a program.
Used to reduce the redundancy of code
Make sure the current directory “my_shared_lib”
Create Makefile file using vim command
vim MakefileContent of Makefile
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk PKG_NAME:=my_shared_lib PKG_VERSION:=1.0 PKG_RELEASE:=1 SOURCE_DIR:=/home/test/openwrt_src/openwrt/package/libs/shared_lib/my_shared_lib include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk define Package/my_shared_lib SECTION:=examples CATEGORY:=Examples TITLE:=My Shared Library endef define Package/my_shared_lib/description A simple shared library example. endef define Build/Prepare mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/src $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/inc $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/obj $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp $(SOURCE_DIR)/Makefile $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $(Build/Patch) endef define Build/Compile $(TARGET_CC) $(TARGET_CFLAGS) -I$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/inc -fPIC -o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/my_shared_lib.o -c $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/src/my_shared_lib.c $(TARGET_CC) $(TARGET_CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC -g -o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/libmy_shared_lib.so $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/my_shared_lib.o endef define Package/my_shared_lib/install $(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/usr/lib $(INSTALL_BIN) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/libmy_shared_lib.so $(1)/usr/lib/ endef $(eval $(call BuildPackage,my_shared_lib))
Explanation of include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
The $(TOPDIR) is expected to be the top-level directory
/rules.mk - The path to the file included
What is $(TOPDIR) ?
See Answer
$(TOPDIR) path is /home/test/openwrt
Explanation of Package Name, Version and Release number Block
PKG_NAME:=my_shared_lib PKG_VERSION:=1.0 PKG_RELEASE:=1
The name and version of your package are used to define the variable to point to the build directory of your package (Ex: my_shared_lib-1.0)
Explanation of SOURCE_DIR
SOURCE_DIR:=$(TOPDIR)/package/libs/shared_lib/my_shared_lib
What is SOURCE_DIR ?
See Answer
SOURCE_DIR is relative or absolute path of directory
In this case path of SOURCE_DIR $HOME/openwrt/package/libs/shared_lib/my_shared_lib
Give path of the source directory
SOURCE_DIR is used in Build/Prepare
Explanation of include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
$(INCLUDE_DIR) - Directory containing include files
/package.mk: The path to the file included
What is $(INCLUDE_DIR) ?
See Answer
$(INCLUDE_DIR) - It will search for included files
In this case path of $(INCLUDE_DIR) $HOME/openwrt/include
Explanation of Package Information
define Package/my_shared_lib SECTION:=examples CATEGORY:=Examples TITLE:=My Shared Library endef
This block defines the package information as section, category, and title
SECTION: examples: This line tells the section to which the package belongs. In this case, the package will come under the “examples” section.
CATEGORY: Examples: This line tells the category to which the package belongs. In this case, the category is set to “Examples
TITLE: My Shared Library This line tells, title or name of the package. In this case, the title is set to “My Shared Library”.
endef: This line will be the end of the define block.
What all information included in Package Information Block ?
See Answer
It includes section, category, and title
Explanation of Package Description
define Package/my_shared_lib/description A simple shared library example endef
This function defines of package.
What is Package Description Block ?
See Answer
Instructs on how and where our package will appear in the overall configuration menu
Explanation of Build/Prepare
define Build/Prepare mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/src $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/inc $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/obj $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp $(SOURCE_DIR)/Makefile $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $(Build/Patch) endef
mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line creates the build directory
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/src $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/inc $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/obj $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)Makefile $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
-r : -r is recursive copy.
$(Build/Patch): This line includes a call to $(Build/Patch), which is a variable or macro typically defined elsewhere in the Makefile. It is used to apply any necessary patches to the source code.
What is -r ?
See Answer
-r is recursive copy.
Which path $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) ?
See Answer
In this case path of $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0
What is SOURCE_DIR ?
See Answer
In this case path of SOURCE_DIR $HOME/openwrt/package/mypackages/examples/my_shared_lib
Explanation of Build/Compile
define Build/Compile $(TARGET_CC) $(TARGET_CFLAGS) -I$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/inc -fPIC -o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/my_shared_lib.o -c $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/src/my_shared_lib.c $(TARGET_CC) $(TARGET_CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC -g -o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/libmy_shared_lib.so $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/my_shared_lib.o endef
This block defines the compilation process.
$(TARGET_CC): It is said to arm cross compiler and it is defined globally
$(TARGET_CFLAGS): It is used for additional flags
-I$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/inc : It will include prototype path
-fPIC: fPIC is to generate position-independent code
-o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/my_shared_lib.o : Takes .c input file location -c $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/src/my_shared_lib.c and generates .o output file in location $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj
-shared: -shared instructs the compiler that we are building a shared library
-g: -g is to leave debugging information in the output file
$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/libmy_shared_lib.so : Takes .o input file location $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/my_shared_lib.o and generates .so output file in location $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj
What is $(TARGET_CC) ?
See Answer
It is said to arm cross compiler
In this case path of $(TARGET_CC) $HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl
What is $(TARGET_CFLAGS) ?
See Answer
It is used for additional flags
Explanation of Package Install
define Package/my_shared_lib/install $(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/usr/lib $(INSTALL_BIN) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/libmy_shared_lib.so $(1)/usr/lib/ endef
$(INSTALL_DIR): It used for creating a directory and it is commonly used in build systems like OpenWrt.
$(INSTALL_BIN): It used for copying an executable file.
In this case path of $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0
/usr/bin: It is the destination directory, .so file will be installed.
What is $(INSTALL_DIR) ?
See Answer
It used for creating a directory
In this case $(INSTALL_DIR) install -d -m0755
Install command is used to copy files and set attributes.
-d, –directory : It will act as directory names towards all arguments.
m, –mode=MODE : Set permission mode (as in chmod).
What is $(INSTALL_BIN) ?
See Answer
It used for copying an executable file.
In this case $(INSTALL_BIN) install -m0755
m, –mode=MODE : Set permission mode (as in chmod).
What is $(1)/usr/bin ?
See Answer
/usr/bin: It is the destination directory where the binary executable will be installed.
In this case path of $(1)/usr/bin $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/.pkgdir/my_shared_lib/usr/lib
Explanation of Package Build
$(eval $(call BuildPackage,my_shared_lib))
BuildPackage: It is function call with my_shared_lib as parameter.
In this section you will learn how to add menuconfig
Make sure the current directory is “openwrt”
Create new feeds.conf file using vim command in openwrt directory
$ vim feeds.conf
Inside feeds.conf
src-link <name> <path>
Make sure the current directory is “openwrt”
Create new feeds.conf file using vim command in openwrt directory
src-link libs /home/test/openwrt/package/libs
In this section you will learn how to install and update feeds
Installs the most recent packages, replacing any earlier versions that were already on your system
$ ./scripts/feeds update -a $ ./scripts/feeds install -a -f
In this section you will learn how to enable in menuconfig
In this section you will learn how to do Pre-build checks
In .config file package should be enabled in ‘y’
Below line should be present in .config file
CONFIG_PACKAGE_my_shared_lib=y
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl
$ ls -l drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Dec 23 02:58 bin drwxr-xr-x 3 test test 4096 Dec 23 03:39 include lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 6 Dec 23 03:39 lib -> ../lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 8 Dec 23 03:20 lib64 -> ../lib64 lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 10 Dec 23 03:39 sys-include -> ../include
Make sure the current directory is “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt $ make package/my_shared_lib/compile
In this section you will learn about post build checks
Make sure the current directory is ‘my_shared_lib-1.0’
$HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0 $ ls -l drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 21:36 inc drwxr-xr-x 3 test test 4096 Jan 8 21:36 ipkg-aarch64_cortex-a72 -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1794 Jan 8 21:36 Makefile drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 21:36 obj drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 21:36 src$ cd src $ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 128 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.c$ cd inc $ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 47 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.h$ cd obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.oSee that object file called my_shared_lib.o is present inside directory ?
See Answer
$HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj
$ ls -l
-rw-r–r– 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
See that .so file called libmy_shared_lib.so is present inside directory ?
See Answer
$HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj
$ ls -l
-rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so
Let check objdump” output of the shared library file
objdump -t : Displays the symbols of application binary file
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “objdump”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/objdump libmy_shared_lib.so -t | grep -i my_shared_function 00000000000004e4 g F .text 0000000000000014 my_shared_function
objdump -S : Display source code intermixed with disassembly
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “objdump”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/objdump libmy_shared_lib.so -S | grep -i my_shared_function 00000000000004e4 <my_shared_function>:
What is “-S” option is used in “objdump” command ?
See Answer
-S : Display source code intermixed with disassembly
What “objdump” command does ?
See Answer
The “objdump” tool is to debug and understand the executable file
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in .so shared library file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
readelf -s: Display the symbol table
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “readelf”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/readelf libmy_shared_lib.so -s | grep -i my_shared_function 7: 00000000000004e4 20 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 9 my_shared_function 60: 00000000000004e4 20 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 9 my_shared_function
What is “-s” option is used in “readelf” command ?
See Answer
-s: Display the symbol table
What “readelf” command does ?
See Answer
readelf: Display information about ELF files
What is the purpose of “readelf” command ?
See Answer
The main purpose of the readelf tool is to display the headers of an ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) files
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in .so shared library file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
nm -S: Print both value and size of defined symbols for the “bsd” output style
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “nm”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/nm libmy_shared_lib.so -S | grep -i my_shared_function 00000000000004e4 0000000000000014 T my_shared_function
What is “-S” option is used in “nm” command ?
See Answer
-S: Print both value and size of defined symbols for the “bsd” output style
What “nm” command does ?
See Answer
nm is used to dump the symbol table and their attributes from a binary executable file.
What is the purpose of “nm” command ?
See Answer
The main purpose of the nm tool is to display information about symbols in the specified File, which can be an object file, an executable file, or an object-file library.
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in .so shared library file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
nm -s: When listing symbols from archive members, include the index: a mapping of which modules contain definitions for which names.
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “nm”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/nm libmy_shared_lib.so -s | grep -i my_shared_function 00000000000004e4 T my_shared_function
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in .so shared library file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
file: Determine file type
$ file libmy_shared_lib.so libmy_shared_lib.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, ARM aarch64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, with debug_info, not stripped
Why “file” command is used ?
See Answer
file command is used to determine the file type.
$ file my_shared_lib.o my_shared_lib.o: ELF 64-bit LSB relocatable, ARM aarch64, version 1 (SYSV), not stripped
size: List section sizes and total size of binary files
$ size libmy_shared_lib.a text data bss dec hex filename 1053 536 56 1645 66d libmy_shared_lib.so
What “size” command does ?
See Answer
size command will display the output that will give you information on the size command in 5 values like data, text, dec, bss, and hex
strings - print the sequences of printable characters in files
As we can see string output are added in the program are confirmed.
$ strings libmy_shared_lib.so | grep -i Hello Hello from my_shared_function!
What “strings” command does ?
See Answer
strings command is used to return the string characters into files.
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/packages/bcm27xx
$ ls -l | grep -i my_shared_lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 123 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk -> /home/test/openwrt/bin/packages/aarch64_cortex-a72/libs/my_shared_lib_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk
ipk file: It is compressed archive format derived from the Debian package (. DEB) format
What is “IPK” file ?
See Answer
IPK file is a compressed archive format derived from the Debian package (. DEB) format
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/packages/bcm27xx
Command to extract .ipk file is below
$ tar -xzf my_shared_lib_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk
$ ls control.tar.gz data.tar.gz debian-binary
what is the command to extract IPK file ?
See Answer
tar -xzf my_shared_lib_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk
First extract control.tar.gz and data.tar.gz
Command to check content for control.tar.gz file is below
$ tar -xzvf control.tar.gz ./control ./postinst ./prerm
Check ./control using “vim command”
$ vim ./control
Content of ./control
Package: my_shared_lib Version: 1.0-1 Depends: libc Source: package/libs/shared_lib/my_shared_lib SourceName: my_shared_lib Section: examples SourceDateEpoch: 1703276774 Architecture: aarch64_cortex-a72 Installed-Size: 1056 Description: A simple shared library example.
Check inside for other files ./postinst and ./prerm using “vim” command
Command to check content for control.tar.gz file is below
$ tar -xzvf data.tar.gz ./usr/ ./usr/lib/ ./usr/lib/libmy_shared_lib.so
Check ./usr/lib/libmy_shared_lib.so is a shared library file
In this section you will learn how to build full openwrt
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt
$ make -j1 V=s
It compile all packages
-j1: This option tells the build system work on one task at a time.
V=s: This sets the verbosity level to ‘s’, which means “silent” or “verbose.” When set to ‘s’, it makes the build system display more detailed information about what it’s doing. You’ll see the commands it’s running and the files it’s working on. This verbose output is helpful for understanding and debugging the build process.
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
To check package is successfully compiled, below is the path
$HOME/openwrt/bin/targets/bcm27xx/bcm2711
To check the image file is present or not
$ ls -l
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1655 Jan 8 21:35 config.buildinfo
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 71 Jan 8 21:35 feeds.buildinfo
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17116537 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17117384 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-sysupgrade.img.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 4210 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4.manifest
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15351092 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-factory.img.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15351939 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-sysupgrade.img.gz
drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 21:37 packages
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 2141 Jan 8 21:37 profiles.json
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 912 Jan 8 21:37 sha256sums
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 18 Jan 8 21:35 version.buildinfo
As we can see “image” is present then it is confirmed that fully image is successfull
Image file is openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
To extract image file command and pathis below
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/bin/targets/bcm27xx/bcm2711
$ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1655 Jan 8 21:35 config.buildinfo -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 71 Jan 8 21:35 feeds.buildinfo -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17116537 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17117384 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-sysupgrade.img.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 4210 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4.manifest -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15351092 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-factory.img.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15351939 Jan 8 21:37 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-sysupgrade.img.gz drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 21:37 packages -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 2141 Jan 8 21:37 profiles.json -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 912 Jan 8 21:37 sha256sums -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 18 Jan 8 21:35 version.buildinfo
Command to extract full image file
$ gunzip -d openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
Content of full image file
The du (disk usage) that allows users to analyze and report on disk usage within directories and files.
Displays sizes in human-readable format, using units such as KB, MB, GB, etc.
$ du -h openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
17M openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
As we can see size of image file is around 17M
Note
PART B: Creating Shared Application
In this section you will learn how to add custom built library in “Openwrt”
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$ pwd /home/test/openwrt
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$ cd package/libs/shared_lib $ mkdir x_shared_app
Make sure the current directory “x_shared_app”
$ cd x_shared_app $ mkdir src obj inc
Make sure the current directory “x_shared_app/src”
In app.c have “Function Definition”
Create app.c file using vim command
vim app.c
Content of src/app.c
#include <stdio.h> #include "my_shared_lib.h" extern void my_shared_function(void); int main(void) { my_shared_function(); return 0; }
Make sure the current directory “x_shared_app/inc”
In my_shared_lib.h have “Function Prototype”
Create my_shared_lib.h file using vim command
vim my_shared_lib.h
Content of inc/my_shared_lib.h
#include <stdio.h> void my_shared_function(void);
Make sure the current directory “x_shared_app”
Create Makefile file using vim command
vim MakefileContent of Makefile
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
PKG_NAME:=x_shared_app PKG_VERSION:=1.0 PKG_RELEASE:=1
SOURCE_DIR:=$(TOPDIR)/package/libs/shared_lib/x_shared_app
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
define Package/x_shared_app SECTION:=examples CATEGORY:=Examples TITLE:=My Shared Library DEPENDS:=+my_shared_lib endef
define Package/x_shared_app/description A simple shared library example. endef
define Build/Prepare mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/src $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/inc $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/obj $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp $(SOURCE_DIR)/Makefile $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $(Build/Patch) endef
define Build/Compile $(TARGET_CC) $(TARGET_CFLAGS) -I$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/inc -L/home/test/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj -o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/app $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/src/app.c -l my_shared_lib endef
define Package/x_shared_app/install $(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/usr/bin $(INSTALL_BIN) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/app $(1)/usr/bin/ endef
$(eval $(call BuildPackage,x_shared_app))
Explanation of include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
The $(TOPDIR) is expected to be the top-level directory
/rules.mk - The path to the file included
What is $(TOPDIR) ?
See Answer
$(TOPDIR) path is /home/test/openwrt
Explanation of Package Name, Version and Release number Block
PKG_NAME:=x_shared_app PKG_VERSION:=1.0 PKG_RELEASE:=1
The name and version of your package are used to define the variable to point to the build directory of your package (Ex: x_shared_app-1.0)
Explanation of SOURCE_DIR
SOURCE_DIR:=$(TOPDIR)/package/libs/shared_lib/x_shared_app
What is SOURCE_DIR ?
See Answer
SOURCE_DIR is relative or absolute path of directory
In this case path of SOURCE_DIR $HOME/openwrt/package/libs/shared_lib/x_shared_app
Give path of the source directory
SOURCE_DIR is used in Build/Prepare
Explanation of include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
$(INCLUDE_DIR) - Directory containing include files
/package.mk: The path to the file included
What is $(INCLUDE_DIR) ?
See Answer
$(INCLUDE_DIR) - It will search for included files
In this case path of $(INCLUDE_DIR) $HOME/openwrt/include
Explanation of Package Information
define Package/x_shared_app SECTION:=examples CATEGORY:=Examples TITLE:=My Shared Library DEPENDS:=+my_shared_lib endef
This block defines the package information as section, category, and title
SECTION: examples: This line tells the section to which the package belongs. In this case, the package will come under the “examples” section.
CATEGORY: Examples: This line tells the category to which the package belongs. In this case, the category is set to “Examples
TITLE: My Shared Library This line tells, title or name of the package. In this case, the title is set to “My Shared Library”.
DEPENDS: =+my_shared_lib: It is the library dependencies of the package.
endef: This line will be the end of the define block.
What all information included in Package Information Block ?
See Answer
It includes section, category, and title
Explanation of Package Description
define Package/x_shared_app/description A simple shared library example endef
This function defines of package.
What is Package Description Block ?
See Answer
Instructs on how and where our package will appear in the overall configuration menu
Explanation of Build/Prepare
define Build/Prepare mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/src $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/inc $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/obj $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) cp $(SOURCE_DIR)/Makefile $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $(Build/Patch) endef
mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line creates the build directory
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/src $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/inc $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)/obj $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
cp -r $(SOURCE_DIR)Makefile $(PKG_BUILD_DIR): This line copies the contents from SOURCE_DIR (source) to PKG_BUILD_DIR (destination)
-r : -r is recursive copy.
$(Build/Patch): This line includes a call to $(Build/Patch), which is a variable or macro typically defined elsewhere in the Makefile. It is used to apply any necessary patches to the source code.
What is -r ?
See Answer
-r is recursive copy.
Which path $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) ?
See Answer
In this case path of $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0
What is SOURCE_DIR ?
See Answer
In this case path of SOURCE_DIR $HOME/openwrt/package/mypackages/examples/x_shared_app
Explanation of Build/Compile
define Build/Compile $(TARGET_CC) $(TARGET_CFLAGS) -I$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/inc -L/home/test/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj -o $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/app $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/src/app.c -l my_shared_lib endef
This block defines the compilation process.
$(TARGET_CC): It is said to arm cross compiler and it is defined globally
-I$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/inc : It will include prototype path
$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/src/app.c : .c file path
-L/home/test/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj : Giving the path of .so file which already generated at “Shared Library” side
l my_shared_lib : It will link during the compilation process (should give 1 space after –l)
How to give path for -L
It is most important to check before giving path in “Shared Application”
Before copying path to –L first we need to check objdump xxxxx.so (in this case libmy_shared_lib.so) with –t or –dSs it will reflect with the symbol table if not symbol table reflect then this path should not be used in –L.
Check table of shared library file
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/my_shared_lib-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 70648 Jan 8 21:36 libmy_shared_lib.so -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1624 Jan 8 21:36 my_shared_lib.o
Check shared library for table
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/objdump libmy_shared_lib.so -dSs | grep -i my_shared_function 00000000000004e4 <my_shared_function>:
We got the table so should give this path(.so file) to -L path in “Shared Application”
What is -L ?
See Answer
-L : It check in directory for library files
What is -l ?
See Answer
-l : It will link with the library files
Explanation of Package Install
define Package/x_shared_app/install $(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/usr/bin $(INSTALL_BIN) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/obj/app $(1)/usr/bin/ endef
$(INSTALL_DIR): It used for creating a directory and it is commonly used in build systems like OpenWrt.
$(INSTALL_BIN): It used for copying an executable file.
In this case path of $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0
/usr/bin: It is the destination directory, binary file will be installed.
What is $(INSTALL_DIR) ?
See Answer
It used for creating a directory
In this case $(INSTALL_DIR) install -d -m0755
Install command is used to copy files and set attributes.
-d, –directory : It will act as directory names towards all arguments.
m, –mode=MODE : Set permission mode (as in chmod).
What is $(INSTALL_BIN) ?
See Answer
It used for copying an executable file.
In this case $(INSTALL_BIN) install -m0755
m, –mode=MODE : Set permission mode (as in chmod).
What is $(1)/usr/bin ?
See Answer
/usr/bin: It is the destination directory where the binary executable will be installed.
In this case path of $(1)/usr/bin $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0/.pkgdir/x_shared_app/usr/bin
Explanation of Package Build
$(eval $(call BuildPackage,x_shared_app))
BuildPackage: It is function call with x_shared_app as parameter.
In this section you will learn how to add menuconfig
Make sure the current directory is “openwrt”
Create new feeds.conf file using vim command in openwrt directory
$ vim feeds.conf
Inside feeds.conf
src-link <name> <path>
Make sure the current directory is “openwrt”
Create new feeds.conf file using vim command in openwrt directory
src-link libs /home/test/openwrt/package/libs
In this section you will learn how to install and update feeds
Installs the most recent packages, replacing any earlier versions that were already on your system
$ ./scripts/feeds update -a $ ./scripts/feeds install -a -f
In this section you will learn how to enable in menuconfig
In this section you will learn how to do Pre-build checks
In .config file package should be enabled in ‘y’
Below line should be present in .config file
CONFIG_PACKAGE_x_shared_app=y
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl
$ ls -l drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Dec 23 02:58 bin drwxr-xr-x 3 test test 4096 Dec 23 03:39 include lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 6 Dec 23 03:39 lib -> ../lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 8 Dec 23 03:20 lib64 -> ../lib64 lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 10 Dec 23 03:39 sys-include -> ../include
Make sure the current directory is “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt $ make package/x_shared_app/compile
In this section you will learn about post build checks
Make sure the current directory is ‘x_shared_app-1.0’
$HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0 $ ls -l drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 23:03 inc drwxr-xr-x 3 test test 4096 Jan 8 23:03 ipkg-aarch64_cortex-a72 -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1280 Jan 8 23:03 Makefile drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 23:03 obj drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 23:03 src$ cd src $ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 141 Jan 8 23:03 app.c$ cd inc $ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 46 Jan 8 23:03 my_shared_lib.h$ cd obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 72736 Jan 8 23:03 app
Let check objdump” output of the shared application file
objdump -t : Displays the symbols of application binary file
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “objdump”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 72736 Jan 8 23:03 app
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/objdump app -t | grep my_shared_function 0000000000000000 F *UND* 0000000000000000 my_shared_function
objdump -S : Display source code intermixed with disassembly
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “objdump”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 72736 Jan 8 23:03 app
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/objdump app -S | grep -i my_shared_function 00000000004004f0 <my_shared_functionplt>: 400528: 97fffff2 bl 4004f0 <my_shared_functionplt>
What is “-S” option is used in “objdump” command ?
See Answer
-S : Display source code intermixed with disassembly
What “objdump” command does ?
See Answer
The “objdump” tool is to debug and understand the executable file
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in app binary file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
readelf -s: Display the symbol table
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “readelf”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 72736 Jan 8 23:03 app
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/readelf app -s | grep -i my_shared_function 2: 0000000000000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND my_shared_function 68: 0000000000000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND my_shared_function
What is “-s” option is used in “readelf” command ?
See Answer
-s: Display the symbol table
What “readelf” command does ?
See Answer
readelf: Display information about ELF files
What is the purpose of “readelf” command ?
See Answer
The main purpose of the readelf tool is to display the headers of an ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) files
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in app binary file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
nm -S: Print both value and size of defined symbols for the “bsd” output style
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “nm”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 72736 Jan 8 23:03 app
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/nm app -S | grep -i my_shared_function U my_shared_function
What is “-S” option is used in “nm” command ?
See Answer
-S: Print both value and size of defined symbols for the “bsd” output style
What “nm” command does ?
See Answer
nm is used to dump the symbol table and their attributes from a binary executable file.
What is the purpose of “nm” command ?
See Answer
The main purpose of the nm tool is to display information about symbols in the specified File, which can be an object file, an executable file, or an object-file library.
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in binary file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
nm -s: When listing symbols from archive members, include the index: a mapping of which modules contain definitions for which names.
Check if “my_shared_function” is present or not in the “nm”
Make sure the current directory “obj”
$ pwd $HOME/openwrt/build_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a72_musl/x_shared_app-1.0/obj $ ls -l -rwxr-xr-x 1 test test 72736 Jan 8 23:03 app
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/toolchain-aarch64_cortex-a72_gcc-12.3.0_musl/aarch64-openwrt-linux-musl/bin/nm app -s | grep -i my_shared_function U my_shared_function
Symbols “my_shared_function” are present in binary application file
Hence we can confirm application is compiled successfully
file: Determine file type
$ file app app: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, ARM aarch64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-musl-aarch64.so.1, with debug_info, not stripped
Why “file” command is used ?
See Answer
file command is used to determine the file type.
size: List section sizes and total size of binary files
$ size app text data bss dec hex filename 1144 664 56 1864 748 app
What “size” command does ?
See Answer
size command will display the output that will give you information on the size command in 5 values like data, text, dec, bss, and hex
strings - print the sequences of printable characters in files
As we can see string output are added in the program are confirmed.
$ strings app | grep -i my_shared_function my_shared_function my_shared_function
What “strings” command does ?
See Answer
strings command is used to return the string characters into files.
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/packages/bcm27xx
$ ls -l | grep -i "x_shared_app" lrwxrwxrwx 1 test test 122 Jan 8 22:45 x_shared_app_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk -> /home/test/openwrt/bin/packages/aarch64_cortex-a72/libs/x_shared_app_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk
ipk file: It is compressed archive format derived from the Debian package (. DEB) format
What is “IPK” file ?
See Answer
IPK file is a compressed archive format derived from the Debian package (. DEB) format
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/staging_dir/packages/bcm27xx
Command to extract .ipk file is below
$ tar -xzf x_shared_app_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk
$ ls control.tar.gz data.tar.gz debian-binary
what is the command to extract IPK file ?
See Answer
tar -xzf helloworld_1.0-1_aarch64_cortex-a72.ipk
First extract control.tar.gz and data.tar.gz
Command to check content for control.tar.gz file is below
$ tar -xzvf control.tar.gz ./control ./postinst ./prerm
Check ./control using “vim command”
$ vim ./control
Content of ./control
Package: x_shared_app Version: 1.0-1 Depends: libc, my_shared_lib Source: package/libs/shared_lib/x_shared_app SourceName: x_shared_app Section: examples SourceDateEpoch: 1703276774 Architecture: aarch64_cortex-a72 Installed-Size: 1201 Description: A simple shared library example.
Check inside for other files ./postinst and ./prerm using “vim” command
Command to check content for control.tar.gz file is below
$ tar -xzvf data.tar.gz ./usr/ ./usr/bin/ ./usr/bin/app
Check ./usr/bin/app is a shared application binary file
In this section you will learn how to build full openwrt
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt
$ make -j1 V=s
It compile all packages
-j1: This option tells the build system work on one task at a time.
V=s: This sets the verbosity level to ‘s’, which means “silent” or “verbose.” When set to ‘s’, it makes the build system display more detailed information about what it’s doing. You’ll see the commands it’s running and the files it’s working on. This verbose output is helpful for understanding and debugging the build process.
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
To check package is successfully compiled, below is the path
$HOME/openwrt/bin/targets/bcm27xx/bcm2711
To check the image file is present or not
$ ls -l
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1685 Jan 8 22:44 config.buildinfo
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 71 Jan 8 22:44 feeds.buildinfo
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17118327 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17119174 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-sysupgrade.img.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 4231 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4.manifest
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15351852 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-factory.img.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15352699 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-sysupgrade.img.gz
drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 22:45 packages
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 2141 Jan 8 22:45 profiles.json
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 912 Jan 8 22:46 sha256sums
-rw-r--r-- 1 test test 18 Jan 8 22:44 version.buildinfo
As we can see “image” is present then it is confirmed that fully image is successfull
Image file is openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
To extract image file command and pathis below
Make sure the current directory “openwrt”
$HOME/openwrt/bin/targets/bcm27xx/bcm2711
$ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 1685 Jan 8 22:44 config.buildinfo -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 71 Jan 8 22:44 feeds.buildinfo -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17118327 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 17119174 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-sysupgrade.img.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 4231 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4.manifest -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15351852 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-factory.img.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 15352699 Jan 8 22:45 openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-squashfs-sysupgrade.img.gz drwxr-xr-x 2 test test 4096 Jan 8 22:45 packages -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 2141 Jan 8 22:45 profiles.json -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 912 Jan 8 22:46 sha256sums -rw-r--r-- 1 test test 18 Jan 8 22:44 version.buildinfo
Command to extract full image file
$ gunzip -d openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
Content of full image file
The du (disk usage) that allows users to analyze and report on disk usage within directories and files.
Displays sizes in human-readable format, using units such as KB, MB, GB, etc.
$ du -h openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz 17M openwrt-bcm27xx-bcm2711-rpi-4-ext4-factory.img.gz
As we can see size of image file is around 17M