HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It is the secure version of HTTP, used for safe communication over the internet. HTTPS encrypts the data exchanged between your browser and a website using SSL/TLS, protecting it from eavesdropping and tampering.
Why is HTTPS useful?
Encrypts data – Protects sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details.
Authenticates websites – Ensures you’re connecting to the real website, not a fake one.
Builds trust – Browsers show a padlock icon for HTTPS sites, signaling safety.
Enables modern web features – Required for things like geolocation, service workers, and secure cookies.
How it works?
Browser connects to a website – It requests a secure connection using HTTPS.
TLS handshake happens – The server presents a digital certificate, and both sides agree on encryption keys.
Secure session starts – All data exchanged is encrypted.
Data is sent and received – Just like HTTP, but now it’s protected from spying or tampering.
Where is HTTPS used?
Banking and e-commerce – To protect financial transactions.
Login pages – To secure usernames and passwords.
Email and messaging apps – For private communication.
Any modern website – HTTPS is now the standard for all secure web traffic.
Why OSI Layer: Application Layer (Layer 7)?
HTTPS builds on HTTP, which is an application-level protocol.
It delivers secure web services directly to users and applications.
The encryption (TLS) occurs below at the Presentation Layer, but HTTPS itself operates at Layer 7.
Is HTTPS Windows specific?
No, HTTPS is not Windows-specific.
HTTPS is a protocol supported across all operating systems, including Windows, Linux, macOS, and mobile devices.
Web browsers and servers on these platforms use HTTPS to transmit encrypted web pages and data securely.
Is HTTPS Linux specific?
No, HTTPS is not Linux-specific.
HTTPS works across multiple platforms, including Linux, Windows, macOS, and mobile platforms.
HTTPS is implemented on web servers (like Apache, Nginx) and browsers on Linux to ensure encrypted communication.
Which Transport Protocol is used by HTTPS?
HTTPS uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) as its transport protocol.
It also relies on SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer / Transport Layer Security) protocols to encrypt data between the client and the server.
Which Port is used by HTTPS?
HTTPS uses TCP port 443 by default.
This port is specifically designated for encrypted HTTP traffic (using SSL/TLS).
Is HTTPS using Client-server model?
Yes, HTTPS uses the client-server model.
The client (usually a web browser) sends a secure request to the server over HTTPS.
The server processes the request and returns the encrypted resource (such as a webpage) back to the client.
Topics in this section,
In this section, you are going to learn
Terminology
Version Info
TLS version |
Authentication |
Encryption |
Encryption Algorithm |
No.of frames |
Wireshark |
Conf file |
Readme |
|
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
4 |
||||
1.2 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 |
ChaCha20 stream cipher + Poly1305 MAC |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 |
ChaCha20 stream cipher + Poly1305 MAC |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.2 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 |
ChaCha20 stream cipher + Poly1305 MAC |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
X.509 Server Certificate+signature |
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 |
ChaCha20 stream cipher + Poly1305 MAC |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
PSK / PSK-DHE |
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 |
ChaCha20 stream cipher + Poly1305 MAC |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-256 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
AES-128 in CBC mode |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
1.3 |
Anonymous Authentication |
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 |
ChaCha20 stream cipher + Poly1305 MAC |
10 |
NO |
Handshake failure. |
||
HTTPS Version |
RFC |
Year |
Core Idea / Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
HTTPS v1.0 |
|||
RFC 2818 |
2000 |
Defined how HTTP is layered over TLS (formerly SSL). Introduced the https:// URI scheme. |
|
HTTPS v1.1 |
|||
RFC 7230 + RFC 2818 |
2014 |
Used HTTP/1.1 over TLS; improved connection reuse and header handling. |
|
HTTPS v2.0 |
|||
RFC 7540 + RFC 2818 |
2015 |
Introduced HTTP/2 over TLS with multiplexing, binary framing, and HPACK header compression. |
|
HTTPS v3.0 |
|||
RFC 9114 |
2022 |
Runs HTTP/3 over QUIC instead of TCP, enabling faster, more reliable secure connections. |
setup
test:~$ curl https://c-pointers.com
Expected output:The HTML source code of the webpage hosted at https://c-pointers.com
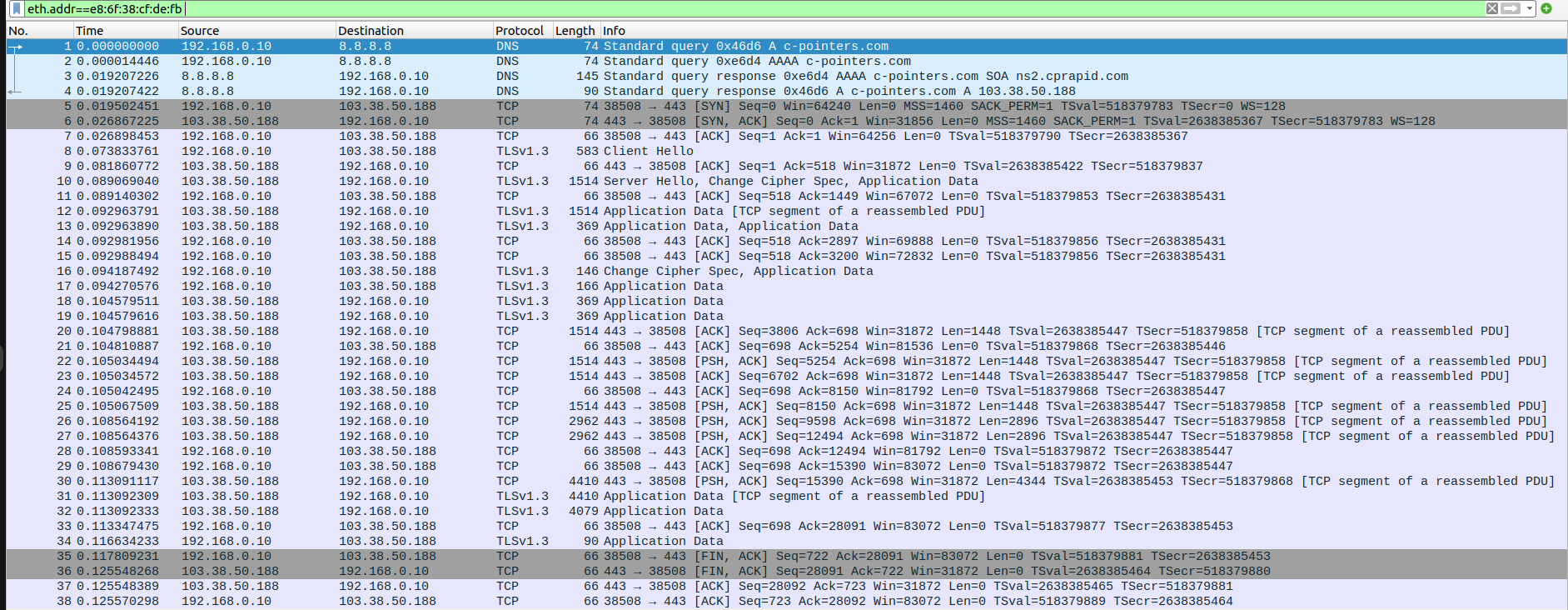
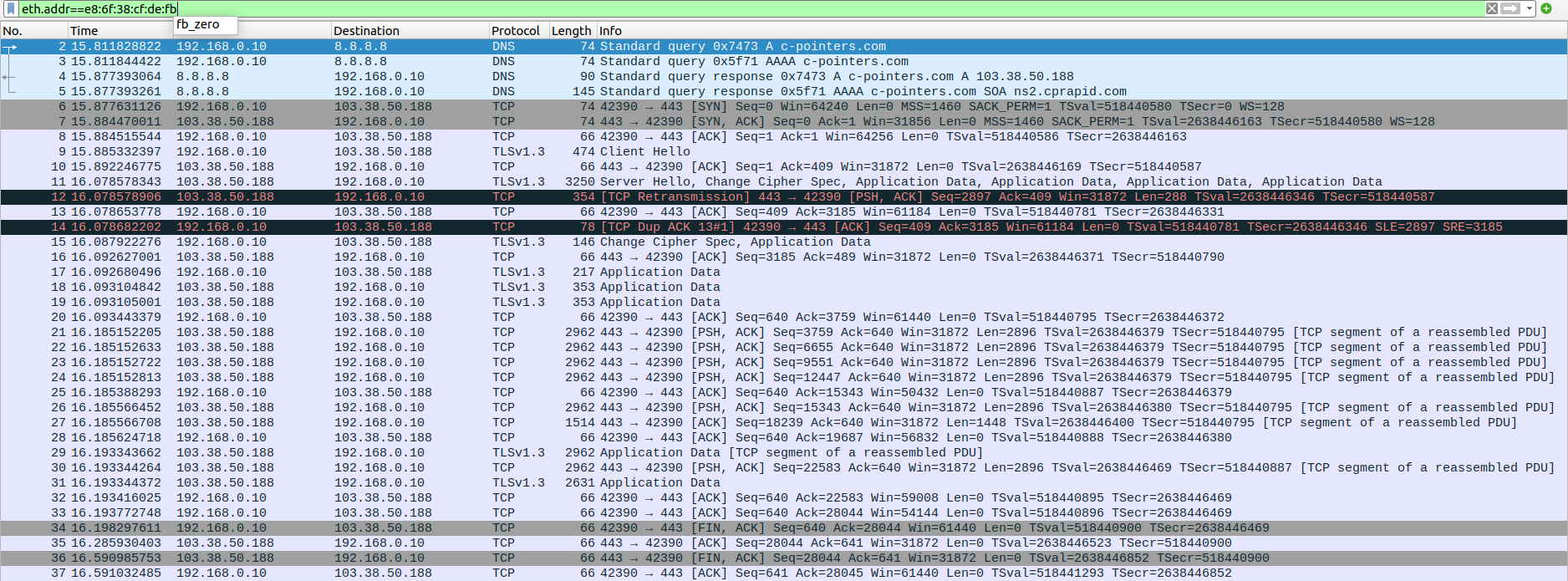
Step-1 : wireshark captures
client side
Step-2 : screenshots
test:~$ wget https://c-pointers.com
Expected output:The HTML content of the webpage at https://c-pointers.com
Step-1 : wireshark captures
client side
Step-2 : screenshots
Step-1: Install Apache Web Server
test:~$ sudo apt update test:~$ sudo apt install apache2 -yStep-2: Adjust the Firewall
1.Check available apache UFW profiles:
test:~$ sudo ufw app list Available applications: Apache Apache Full Apache Secure2.You want to allow both http and https,so Apache Full is a good choice.
test:~$ sudo ufw allow 'Apache Full'Step-3: Verify apache service
test:~$ sudo systemctl start apache2 test:~$ sudo systemctl enable apache2 test:~$ sudo systemctl status apache2Step-4: Test your Webserver
Open your webserver and navigate to your server’s IP address like http://10.91.239.125
To check in terminal also
test:~$ curl -v http://10.91.239.125You should see the default apache ubuntu page.This confirms that apache is installed and running correctly.
Note
10.91.239.125 is the your’s server IP address of Ubuntu Machine.
Step-5: Lets create your own domain.com
Create a directory for your domain:
test:~$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/myuniqueproxy.com/htmlNote
myuniqueproxy.com is my own domain.com.You can replace with this your’s actual domain.com.
Create a sample index.html file
test:~$ sudo nano /var/www/myuniqueproxy.com/html/index.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to myuniqueproxy.com domain</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello from my own web server!</h1> <p>This page is hosted on Apache running on Ubuntu.</p> </body> </html>Save the file (Ctrl+O, Enter, Ctrl+X).
Note
You want to add some more context.You can add in index.html file.
Step-6: Set Proper permissions
test:~$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/myuniqueproxy.com/html test:~$ sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/myuniqueproxy.com
Step-7: Enable SSL module and default SSL site
test:~$ sudo a2enmod ssl test:~$ sudo a2ensite default-ssl test:~$ sudo systemctl reload apache2
Step-8: Generate a Self-Signed SSL Certificate
1.Create a directory to store your certificate
test:~$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/apache2/ssl
2.Now generate the certificate and private key
test:~$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/apache2/ssl/apache-selfsigned.key -out /etc/apache2/ssl/apache-selfsigned.crt
Note
You will be prompted to enter values like country, state, etc.Common name section you enter your server IP address.These will appear in your certificate.
Step-9: Configure Apache to Use Your Certificate
Edit the default SSL site:
test:~$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl.conf <IfModule mod_ssl.c> <VirtualHost _default_:443> ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost DocumentRoot /var/www/myuniqueproxy.com/html # ServerName is optional for IP-based access # ServerName your-domain.com ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined # SSL Configuration SSLEngine on SSLProtocol -all +TLSV1.2 SSLCipherSuite RSA+AESGCM SSLCertificateFile /etc/apache2/ssl/apache-selfsigned.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/apache2/ssl/apache-selfsigned.key <FilesMatch "\.(cgi|shtml|phtml|php)$"> SSLOptions +StdEnvVars </FilesMatch> <Directory /usr/lib/cgi-bin> SSLOptions +StdEnvVars </Directory> # Optional security headers Header always set X-Frame-Options DENY Header always set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff Header always set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" # Optional SSL settings (hardened) SSLProtocol all -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1 SSLCipherSuite HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5 SSLHonorCipherOrder on </VirtualHost> </IfModule>
Save and exit (Ctrl+O, Enter, then Ctrl+X).
Note
SSLProtocol -all +TLSV1.2 ,SSLCipherSuite RSA+AESGCM these two lines are support for TLSV1.2 protocol.
If you comment these two lines then it support for TLSV1.3 protocol.
Step-10: Restart Apache
test:~$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step-11: Test Your Server
Open a browser and go to:
Note
You’ll see a warning that the certificate is not trusted — this is expected with a self-signed certificate. You can proceed anyway.
After you observe the your index.html page.
10.91.239.125 is the server IP address
Step -1 : obtain the custom webserver’s certificate
test:~$ echo | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect 10.91.239.125:443
This will show you the certificate chain the custom webserver is presenting.copy the certificate from the output (the blocking starting with —-begin certificate—-and ending with —END CERTIFICATE—).
save it to a file,e.g., ownwebserver.crt
step-2 : ADD the custom webserver certificate to trusted CA store
1.copy the custom webserver certificate to /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
test:~$ sudo cp ownwebserver.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
2.update the certificate store
test:~$ sudo update-ca-certificates
this will add the custom webserver’s self-signed certificate to the list of trusted certificates.
Note
10.91.239.125 is the IP address of custom webserver.
- 1.Set SSLKEYLOGFILE Environment Variable
Set this environment variable to capture the session keys.
test:~$ export SSLKEYLOGFILE=~/noproxy_sslkeys.log
Note
This tells supported TLS libraries to log pre-master secrets into that file.
This only works if the TLS library used by curl supports it (like OpenSSL with debug support or NSS).
- 2.RUN the curl command
test:~$ curl -v https://10.91.239.125
- 3.Start a Wireshark capture
Open Wireshark.
Select the network interface that your traffic goes through (e.g., eth0, wlan0).
Apply a capture filter if you want, or just start the capture.
Run your curl command while capturing is active.
test:~$ curl -v https://10.91.239.125
- 4.Configure Wireshark to use the SSL key log
Go to Edit > Preferences > Protocols > TLS.
Find the field for:
(Pre)-Master-Secret log filename
Set it to the path of your sslkeys.log file, e.g.,/home/user/noproxy_sslkeys.log
Click OK.
Then,Wireshark will use the session keys to decrypt HTTPS traffic.
- 5.View decrypted traffic
You should now see decrypted HTTP requests and responses in plain text!
FILE NAME |
PATH |
DESCRIPTION |
apache-selfsigned.crt |
/etc/apache2/ssl/apache-selfsigned.crt |
Self-signed public certificate used for local or test HTTPS setups. |
apache-selfsigned.key |
/etc/apache2/ssl/apache-selfsigned.key |
Private key matching apache-selfsigned.crt. Needed for SSL/TLS on the server. |
sslkeylogfile |
/home/user/noproxy_sslkeys.log |
File that stores TLS session keys. Used by Wireshark to decrypt HTTPS traffic when SSLKEYLOGFILE is set. |
ownwebserver.crt |
/home/user/ownwebserver.crt |
Public certificate for your web server. Presented to clients during HTTPS connections. |
setup
HTTPS Request Packet
S.No |
Protocol Packets |
Description |
Size(Bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
HTTPS Request Packet |
Sent by the client to initiate a secure connection and request a |
|
resource |
|||
TLS Handshake |
Establishes encryption keys and verifies server identity |
~5001500 |
|
ClientHello |
Includes supported TLS versions, cipher suites, random number |
~200 |
|
ServerHello |
Server responds with chosen cipher suite, certificate |
~300 |
|
Certificate |
Servers digital certificate (X.509) |
~1000 |
|
Key Exchange |
Exchange of keys (e.g., Diffie-Hellman parameters) |
~200 |
|
Finished |
Marks end of handshake |
~100 |
|
Encrypted HTTP Request |
Actual HTTP request (GET, POST, etc.) encrypted |
~1000+ |
|
Encrypted Headers |
Host, User-Agent, etc., encrypted |
~200500 |
|
Encrypted Body |
HTML, JSON, etc., encrypted |
Variable (~1000) |
|
HTTPS Response Packet
S.No |
Protocol Packets |
Description |
Size(Bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
HTTPS Response Packet |
Sent by the server in response to the clients encrypted request |
|
Encrypted HTTP Response |
Status line, headers, and body, all encrypted |
~1000+ |
|
Encrypted Status Line |
HTTP/1.1 200 OK, etc. |
~100 |
|
Encrypted Headers |
Content-Type, Set-Cookie, etc. |
~200500 |
|
Encrypted Body |
HTML, JSON, etc. |
Variable (~1000) |
|
TLS Session Resumption (Optional) |
Reduces handshake overhead for future requests |
~100300 |
|
S.no |
Use Case |
Description |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Secure Web Browsing |
HTTPS ensures encrypted communication between browsers and websites, protecting user data and privacy. |
2 |
Secure RESTful APIs |
REST APIs use HTTPS to safeguard data exchange between clients and servers, especially for sensitive information. |
3 |
Mobile Applications |
Mobile apps use HTTPS to securely transmit user data, login credentials, and other sensitive information to backend servers. |
4 |
IoT Device Communication |
HTTPS secures communication between IoT devices and cloud servers, preventing data interception and tampering. |
5 |
Cloud Services |
HTTPS is essential for secure access to cloud-based applications, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. |
6 |
Secure File Downloads |
HTTPS protects file downloads from tampering and ensures the authenticity of the source. |
7 |
Webhooks |
HTTPS is used for secure webhook delivery, ensuring that notifications are encrypted and verified. |
8 |
Proxy and Caching |
HTTPS headers and TLS certificates help manage secure caching and proxy behavior, ensuring data is not exposed or altered. |
S.no |
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Encryption |
Encrypts data in transit using SSL/TLS to prevent eavesdropping. |
2 |
Data Integrity |
Ensures that data is not altered or tampered with during transmission. |
3 |
Authentication |
Verifies the identity of the website using digital certificates (SSL/TLS). |
4 |
Secure Port (443) |
Uses port 443 by default for secure communication. |
5 |
Certificate-Based Trust |
Relies on trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) to issue and validate certificates. |
6 |
Protection Against MITM |
Prevents man-in-the-middle attacks by encrypting the communication channel. |
7 |
SEO and Browser |
HTTPS-enabled sites are favored by search engines and marked secure by browsers. |
Preference |
||
8 |
Forward Secrecy |
Uses ephemeral keys to ensure past sessions remain secure even if keys are compromised. |
9 |
Compatibility with HTTP |
Maintains the same request/response structure as HTTP, making it easy to upgrade. |
10 |
Required for Modern |
Needed for features like HTTP/2, service workers, and progressive web apps (PWAs). |
Features |
Encryption - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Access HTTPS Website |
Open https://example.com |
Data encrypted in transit |
2 |
Use TLS 1.2 |
Server supports TLS 1.2 |
Secure connection established |
3 |
Use TLS 1.3 |
Server supports TLS 1.3 |
Secure connection established |
4 |
Use SSL Labs Test |
Scan HTTPS site |
Encryption strength reported |
5 |
Use Encrypted Login |
Submit credentials over HTTPS |
Data encrypted |
6 |
Use Encrypted Form Submission |
Submit form data |
Data not visible in transit |
7 |
Use HTTPS with API |
Call REST API |
Request and response encrypted |
8 |
Use HTTPS with WebSocket |
Use wss:// |
Encrypted WebSocket connection |
9 |
Use HTTPS with CDN |
Content served via HTTPS |
Data encrypted end-to-end |
10 |
Use HTTPS with Reverse Proxy |
TLS terminates at proxy |
Data encrypted to proxy |
11 |
Use HTTPS with Load Balancer |
TLS terminates at load balancer |
Secure connection maintained |
12 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile App |
App connects via HTTPS |
Data encrypted |
13 |
Use HTTPS with Desktop App |
App uses HTTPS for API |
Secure communication |
14 |
Use HTTPS with IoT Device |
Device sends data via HTTPS |
Data encrypted |
15 |
Use HTTPS with Browser Extension |
Extension uses HTTPS |
Secure data exchange |
16 |
Use HTTPS with CLI Tool |
Use curl/wget with HTTPS |
Data encrypted |
17 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Pinning |
Client validates cert fingerprint |
Prevents MITM attacks |
18 |
Use HTTPS with Mutual TLS |
Client and server authenticate |
Secure two-way connection |
19 |
Use HTTPS with OCSP Stapling |
Server provides OCSP response |
Certificate validated securely |
20 |
Use HTTPS with SNI |
Multiple domains on one IP |
Correct cert served securely |
21 |
Use HTTPS with DNS over HTTPS |
Secure DNS resolution |
Queries encrypted |
22 |
Use HTTPS with TLS Session Resumption |
Reuse session |
Secure and fast |
23 |
Use HTTPS with Forward Secrecy |
Use ephemeral keys |
Past sessions safe |
24 |
Use HTTPS with Encrypted SNI |
Hide domain in handshake |
Prevents SNI leaks |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Transparency |
Cert logged in CT logs |
Increases trust |
26 |
Use HTTPS with Secure Cookies |
Cookies marked Secure |
Sent only over HTTPS |
27 |
Use HTTPS with CSP |
Content Security Policy enforced |
Secure content loading |
28 |
Use HTTPS with HSTS |
Enforce HTTPS |
Prevents downgrade attacks |
29 |
Use HTTPS with Secure Headers |
Use X-Content-Type-Options, etc. |
Enhanced security |
30 |
Use HTTPS with Payment Gateway |
Submit payment info |
Data encrypted |
31 |
Use HTTPS with OAuth |
Token exchange over HTTPS |
Tokens protected |
32 |
Use HTTPS with SSO |
Single sign-on via HTTPS |
Secure authentication |
33 |
Use HTTPS with File Upload |
Upload files securely |
Data encrypted in transit |
34 |
Use HTTPS with File Download |
Download files securely |
Data encrypted in transit |
35 |
Use HTTPS with Email API |
Send email via HTTPS |
Secure transmission |
36 |
Use HTTPS with Analytics |
Send data securely |
Data encrypted |
37 |
Use HTTPS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor HTTPS traffic |
Valid cert and cipher shown |
38 |
Use HTTPS with Logging Tool |
Log HTTPS requests |
Sensitive data encrypted |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Rate Limiting |
Apply limits over HTTPS |
Limits enforced securely |
40 |
Use HTTPS with CDN Edge Node |
Connect to nearest secure node |
Fast and secure delivery |
41 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site |
Serve static files securely |
Files load over HTTPS |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Dynamic Site |
Serve dynamic content |
Secure connection |
43 |
Use HTTPS with Redirect |
Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS |
Secure connection enforced |
44 |
Use HTTPS with Browser Warning |
Access site with invalid cert |
Browser blocks access |
45 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Renewal |
Renew expiring cert |
Secure connection maintained |
46 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Authority |
Use trusted CA |
Certificate trusted by browsers |
47 |
Use HTTPS with Wildcard Certificate |
Secure multiple subdomains |
All subdomains encrypted |
48 |
Use HTTPS with SAN Certificate |
Secure multiple domains |
All domains encrypted |
49 |
Use HTTPS with Cloud Gateway |
Route through secure gateway |
Data encrypted |
50 |
Use HTTPS with VPN |
Tunnel HTTPS over VPN |
Double encryption in transit |
Data Integrity - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Send Encrypted Request |
Use HTTPS for API call |
Data arrives unaltered |
2 |
Send Encrypted Form Data |
Submit form over HTTPS |
Server receives exact data |
3 |
Send Encrypted File Upload |
Upload file via HTTPS |
File integrity preserved |
4 |
Download File via HTTPS |
Download file securely |
File matches original |
5 |
Use TLS Handshake |
Establish secure session |
Integrity checks enabled |
6 |
Use MAC in TLS Record |
TLS uses MAC |
Tampered data rejected |
7 |
Use SHA-256 in TLS |
TLS uses strong hash |
Data integrity ensured |
8 |
Use HTTPS with API Gateway |
Route through gateway |
Payload not altered |
9 |
Use HTTPS with CDN |
Serve content via HTTPS |
Content not modified |
10 |
Use HTTPS with Reverse Proxy |
Proxy forwards data |
Data remains intact |
11 |
Use HTTPS with Load Balancer |
Load balancer handles TLS |
Data integrity preserved |
12 |
Use HTTPS with WebSocket |
Use wss:// |
Messages not tampered |
13 |
Use HTTPS with OAuth |
Token exchange over HTTPS |
Tokens not altered |
14 |
Use HTTPS with SSO |
SSO tokens transmitted securely |
Tokens verified |
15 |
Use HTTPS with Payment Gateway |
Submit payment info |
Transaction data intact |
16 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Pinning |
Validate server cert |
Prevents MITM tampering |
17 |
Use HTTPS with Mutual TLS |
Both ends authenticate |
Data integrity verified |
18 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.3 |
Use latest TLS version |
Strongest integrity checks |
19 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.2 |
Use secure TLS version |
Data integrity ensured |
20 |
Use HTTPS with OCSP Stapling |
Validate cert status |
Prevents forged certs |
21 |
Use HTTPS with Encrypted SNI |
Hide domain info |
Prevents tampering in handshake |
22 |
Use HTTPS with Forward Secrecy |
Use ephemeral keys |
Past data protected |
23 |
Use HTTPS with Session Resumption |
Resume TLS session |
Integrity checks maintained |
24 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site |
Serve HTML/CSS/JS |
Files not modified in transit |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Dynamic Site |
Serve API responses |
Data integrity preserved |
26 |
Use HTTPS with JSON API |
Send JSON payload |
No data corruption |
27 |
Use HTTPS with XML API |
Send XML payload |
No data corruption |
28 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile App |
App communicates securely |
Data not altered |
29 |
Use HTTPS with Desktop App |
App uses HTTPS |
Data integrity ensured |
30 |
Use HTTPS with IoT Device |
Device sends telemetry |
Data received as sent |
31 |
Use HTTPS with CLI Tool |
Use curl/wget |
Data matches source |
32 |
Use HTTPS with Browser |
Load secure page |
HTML/JS not tampered |
33 |
Use HTTPS with File Hash Check |
Compare hash after download |
Hashes match |
34 |
Use HTTPS with CSP |
Prevent script injection |
Content integrity enforced |
35 |
Use HTTPS with HSTS |
Enforce HTTPS |
Prevents downgrade attacks |
36 |
Use HTTPS with Secure Headers |
Use X-Content-Type-Options |
Prevents MIME sniffing |
37 |
Use HTTPS with Logging Tool |
Log HTTPS traffic |
Logs show unaltered data |
38 |
Use HTTPS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor HTTPS sessions |
No tampering detected |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Analytics |
Send metrics securely |
Data not modified |
40 |
Use HTTPS with CDN Edge |
Serve from edge node |
Content integrity preserved |
41 |
Use HTTPS with Redirect |
Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS |
Secure path enforced |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Transparency |
Certs logged |
Prevents forged certs |
43 |
Use HTTPS with Wildcard Cert |
Secure subdomains |
Data integrity ensured |
44 |
Use HTTPS with SAN Cert |
Secure multiple domains |
Data not altered |
45 |
Use HTTPS with VPN |
Tunnel HTTPS over VPN |
Double integrity protection |
46 |
Use HTTPS with Firewall |
Inspect encrypted traffic |
No data tampering |
47 |
Use HTTPS with DDoS Protection |
Filter traffic |
Valid data preserved |
48 |
Use HTTPS with Rate Limiting |
Enforce limits securely |
Data not dropped or altered |
49 |
Use HTTPS with Retry Logic |
Retry failed requests |
Data integrity maintained |
50 |
Use HTTPS with Compression |
Compress and send data |
Decompressed data matches original |
Authentication - Testcases
s.no |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Access HTTPS Site with Valid Certificate |
Open secure website |
Browser shows padlock |
2 |
Access Site with Self-Signed Certificate |
Use self-signed cert |
Browser shows warning |
3 |
Access Site with Expired Certificate |
Certificate is expired |
Browser blocks access |
4 |
Access Site with Revoked Certificate |
Certificate is revoked |
Browser shows error |
5 |
Access Site with Mismatched Domain |
Cert domain URL |
Browser shows warning |
6 |
Access Site with Valid CA Certificate |
Cert issued by trusted CA |
Browser trusts site |
7 |
Access Site with Untrusted CA |
Cert from unknown CA |
Browser shows untrusted warning |
8 |
Use TLS Handshake |
Initiate HTTPS connection |
Server presents certificate |
9 |
Verify Certificate Chain |
Check intermediate certs |
Full chain validated |
10 |
Use Certificate Transparency |
Cert logged in CT logs |
Browser accepts cert |
11 |
Use OCSP Stapling |
Server provides OCSP response |
Faster revocation check |
12 |
Use CRL Check |
Client checks revocation list |
Revoked certs rejected |
13 |
Use Wildcard Certificate |
Secure *.example.com |
All subdomains authenticated |
14 |
Use SAN Certificate |
Secure multiple domains |
All listed domains trusted |
15 |
Use EV Certificate |
Extended Validation cert |
Green bar or org name shown |
16 |
Use DV Certificate |
Domain Validation cert |
Basic identity verified |
17 |
Use OV Certificate |
Organization Validation cert |
Org identity verified |
18 |
Use Certificate Pinning |
Client checks cert fingerprint |
Prevents MITM |
19 |
Use Mutual TLS |
Client and server authenticate |
Two-way trust established |
20 |
Use HTTPS with API Gateway |
Gateway verifies cert |
Secure backend routing |
21 |
Use HTTPS with Load Balancer |
TLS terminates at LB |
Cert validated at entry point |
22 |
Use HTTPS with Reverse Proxy |
Proxy validates cert |
Secure connection |
23 |
Use HTTPS with CDN |
CDN presents valid cert |
Client trusts connection |
24 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile App |
App validates server cert |
Secure communication |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Desktop App |
App checks cert chain |
Trusted connection |
26 |
Use HTTPS with IoT Device |
Device validates cert |
Secure telemetry |
27 |
Use HTTPS with Browser Extension |
Extension checks cert |
Secure data exchange |
28 |
Use HTTPS with CLI Tool |
curl/wget validate cert |
Connection succeeds if valid |
29 |
Use HTTPS with SSO |
Identity provider cert validated |
Secure login |
30 |
Use HTTPS with OAuth |
Token server cert validated |
Secure token exchange |
31 |
Use HTTPS with Payment Gateway |
Gateway cert validated |
Secure transaction |
32 |
Use HTTPS with Email API |
Cert validated before sending |
Secure email delivery |
33 |
Use HTTPS with WebSocket |
wss:// uses TLS cert |
Secure handshake |
34 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.3 |
Latest protocol used |
Strong authentication |
35 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.2 |
Secure protocol used |
Cert validated |
36 |
Use HTTPS with SNI |
Cert selected based on hostname |
Correct cert served |
37 |
Use HTTPS with Encrypted SNI |
Hide domain in handshake |
Prevents SNI-based attacks |
38 |
Use HTTPS with VPN |
HTTPS over VPN |
Double authentication layer |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Firewall |
Cert validated before inspection |
Secure access |
40 |
Use HTTPS with Proxy |
Proxy validates cert |
Secure routing |
41 |
Use HTTPS with Rate Limiting |
Authenticated requests limited |
Secure enforcement |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Logging Tool |
Log cert details |
Certificate chain recorded |
43 |
Use HTTPS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor cert validity |
Alerts on expiry |
44 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Renewal |
Renew before expiry |
Continuous authentication |
45 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Rotation |
Rotate certs periodically |
Authentication maintained |
46 |
Use HTTPS with Cloud Gateway |
Gateway presents valid cert |
Secure cloud access |
47 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site |
Cert validates domain |
Trusted content |
48 |
Use HTTPS with Dynamic Site |
Cert validates backend |
Secure data exchange |
49 |
Use HTTPS with Analytics |
Cert validates endpoint |
Secure metrics collection |
50 |
Use HTTPS with Health Check |
Validate cert during check |
Secure status monitoring |
SecurePort(443) - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Access HTTPS Site on Port 443 |
Open https://example.com |
Connects via port 443 |
2 |
Access HTTPS Site with Explicit Port |
Connection succeeds |
|
3 |
Access HTTPS Site on Port 80 |
Connection fails or insecure |
|
4 |
Access HTTP Site on Port 443 |
Connection fails |
|
5 |
Block Port 443 in Firewall |
Try to access HTTPS site |
Connection blocked |
6 |
Allow Port 443 in Firewall |
Access HTTPS site |
Connection succeeds |
7 |
Use HTTPS with Load Balancer on Port 443 |
Load balancer listens on 443 |
Secure traffic routed |
8 |
Use HTTPS with Reverse Proxy on Port 443 |
Proxy listens on 443 |
Secure connection established |
9 |
Use HTTPS with CDN on Port 443 |
CDN serves content |
Secure delivery via 443 |
10 |
Use HTTPS with API Gateway on Port 443 |
API exposed on 443 |
Secure API access |
11 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile App |
App connects via port 443 |
Secure communication |
12 |
Use HTTPS with Desktop App |
App uses port 443 |
Data encrypted |
13 |
Use HTTPS with IoT Device |
Device sends data on 443 |
Secure telemetry |
14 |
Use HTTPS with WebSocket |
Use wss:// on port 443 |
Secure WebSocket connection |
15 |
Use HTTPS with VPN Tunnel |
HTTPS over VPN |
Port 443 used securely |
16 |
Use HTTPS with Proxy |
Proxy forwards via 443 |
Secure routing |
17 |
Use HTTPS with NAT Gateway |
NAT maps to port 443 |
Secure access maintained |
18 |
Use HTTPS with Port Forwarding |
Forward 443 to internal server |
Secure connection established |
19 |
Use HTTPS with Port Scanner |
Scan for open ports |
Port 443 detected as open |
20 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.3 on Port 443 |
Secure handshake |
Connection encrypted |
21 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.2 on Port 443 |
Secure handshake |
Connection encrypted |
22 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Validation |
Cert served on 443 |
Identity verified |
23 |
Use HTTPS with Mutual TLS |
Auth on port 443 |
Two-way authentication |
24 |
Use HTTPS with OCSP Stapling |
Cert status checked on 443 |
Validation succeeds |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Pinning |
Cert validated on 443 |
Prevents MITM |
26 |
Use HTTPS with SNI |
Multiple certs on 443 |
Correct cert served |
27 |
Use HTTPS with Encrypted SNI |
Domain hidden on 443 |
Privacy preserved |
28 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site |
Serve HTML on 443 |
Secure delivery |
29 |
Use HTTPS with Dynamic Site |
Serve API on 443 |
Secure data exchange |
30 |
Use HTTPS with File Upload |
Upload via 443 |
Data encrypted |
31 |
Use HTTPS with File Download |
Download via 443 |
Data encrypted |
32 |
Use HTTPS with Payment Gateway |
Submit payment on 443 |
Secure transaction |
33 |
Use HTTPS with OAuth |
Token exchange on 443 |
Secure authentication |
34 |
Use HTTPS with SSO |
Login on 443 |
Identity verified |
35 |
Use HTTPS with Analytics |
Send metrics on 443 |
Data encrypted |
36 |
Use HTTPS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor traffic on 443 |
Secure metrics |
37 |
Use HTTPS with Logging Tool |
Log requests on 443 |
Secure logs |
38 |
Use HTTPS with Rate Limiting |
Enforce limits on 443 |
Secure enforcement |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Firewall Rules |
Allow only port 443 |
Secure access only |
40 |
Use HTTPS with Port Redirection |
Redirect 80 to 443 |
Secure connection enforced |
41 |
Use HTTPS with HSTS |
Enforce HTTPS on 443 |
Prevent downgrade |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Secure Headers |
Headers sent on 443 |
Enhanced security |
43 |
Use HTTPS with CSP |
Policy enforced on 443 |
Secure content loading |
44 |
Use HTTPS with Browser |
Browser connects via 443 |
Secure padlock shown |
45 |
Use HTTPS with CLI Tool |
curl uses port 443 |
Secure response received |
46 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Renewal |
Renew cert on 443 |
Secure access maintained |
47 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Transparency |
Cert logged on 443 |
Trust established |
48 |
Use HTTPS with Wildcard Cert |
Secure subdomains on 443 |
All trusted |
49 |
Use HTTPS with SAN Cert |
Secure multiple domains on 443 |
All validated |
50 |
Use HTTPS with Health Check |
Check service on 443 |
Secure status confirmed |
Certificate Based Trust - Testcases
S.no |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Access Site with Valid CA Certificate |
Cert issued by trusted CA |
Browser trusts site |
2 |
Access Site with Untrusted CA |
Cert from unknown CA |
Browser shows warning |
3 |
Access Site with Expired Certificate |
Certificate is expired |
Browser blocks access |
4 |
Access Site with Revoked Certificate |
Certificate is revoked |
Browser shows error |
5 |
Access Site with Mismatched Domain |
Cert domain URL |
Browser shows warning |
6 |
Use Certificate Chain Validation |
Validate root and intermediates |
Full chain trusted |
7 |
Use Root CA Trust Store |
Cert matches trusted root |
Connection succeeds |
8 |
Use Intermediate CA |
Cert issued via intermediate |
Chain validated successfully |
9 |
Use Certificate Transparency |
Cert logged in CT logs |
Browser accepts cert |
10 |
Use OCSP Stapling |
Server provides OCSP response |
Revocation status verified |
11 |
Use CRL Check |
Client checks revocation list |
Revoked cert rejected |
12 |
Use Wildcard Certificate |
Secure *.example.com |
All subdomains trusted |
13 |
Use SAN Certificate |
Secure multiple domains |
All listed domains trusted |
14 |
Use EV Certificate |
Extended Validation cert |
Organization name shown |
15 |
Use DV Certificate |
Domain Validation cert |
Basic identity verified |
16 |
Use OV Certificate |
Organization Validation cert |
Org identity verified |
17 |
Use Certificate Pinning |
Client checks cert fingerprint |
Prevents MITM |
18 |
Use Mutual TLS |
Both client and server authenticate |
Two-way trust established |
19 |
Use TLS Handshake |
Server presents certificate |
Identity verified |
20 |
Use HTTPS with API Gateway |
Gateway validates cert |
Secure backend routing |
21 |
Use HTTPS with Load Balancer |
TLS terminates at LB |
Cert validated at entry point |
22 |
Use HTTPS with Reverse Proxy |
Proxy validates cert |
Secure connection |
23 |
Use HTTPS with CDN |
CDN presents valid cert |
Client trusts connection |
24 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile App |
App validates server cert |
Secure communication |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Desktop App |
App checks cert chain |
Trusted connection |
26 |
Use HTTPS with IoT Device |
Device validates cert |
Secure telemetry |
27 |
Use HTTPS with Browser Extension |
Extension checks cert |
Secure data exchange |
28 |
Use HTTPS with CLI Tool |
curl/wget validate cert |
Connection succeeds if valid |
29 |
Use HTTPS with SSO |
Identity provider cert validated |
Secure login |
30 |
Use HTTPS with OAuth |
Token server cert validated |
Secure token exchange |
31 |
Use HTTPS with Payment Gateway |
Gateway cert validated |
Secure transaction |
32 |
Use HTTPS with Email API |
Cert validated before sending |
Secure email delivery |
33 |
Use HTTPS with WebSocket |
wss:// uses TLS cert |
Secure handshake |
34 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.3 |
Latest protocol used |
Strong authentication |
35 |
Use HTTPS with TLS 1.2 |
Secure protocol used |
Cert validated |
36 |
Use HTTPS with SNI |
Cert selected based on hostname |
Correct cert served |
37 |
Use HTTPS with Encrypted SNI |
Domain hidden in handshake |
Prevents SNI-based attacks |
38 |
Use HTTPS with VPN |
HTTPS over VPN |
Double authentication layer |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Firewall |
Cert validated before inspection |
Secure access |
40 |
Use HTTPS with Proxy |
Proxy validates cert |
Secure routing |
41 |
Use HTTPS with Rate Limiting |
Authenticated requests limited |
Secure enforcement |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Logging Tool |
Log cert details |
Certificate chain recorded |
43 |
Use HTTPS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor cert validity |
Alerts on expiry |
44 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Renewal |
Renew before expiry |
Continuous authentication |
45 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Rotation |
Rotate certs periodically |
Authentication maintained |
46 |
Use HTTPS with Cloud Gateway |
Gateway presents valid cert |
Secure cloud access |
47 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site |
Cert validates domain |
Trusted content |
48 |
Use HTTPS with Dynamic Site |
Cert validates backend |
Secure data exchange |
49 |
Use HTTPS with Analytics |
Cert validates endpoint |
Secure metrics collection |
50 |
Use HTTPS with Health Check |
Validate cert during check |
Secure status monitoring |
Protection Against MITM Attack - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Access HTTPS Site |
Open secure website |
Data encrypted, MITM blocked |
2 |
Use TLS Handshake |
Establish secure session |
Identity verified, MITM prevented |
3 |
Use Valid Certificate |
Trusted CA cert used |
Browser trusts connection |
4 |
Use Certificate Pinning |
Client checks cert fingerprint |
MITM with fake cert blocked |
5 |
Use Mutual TLS |
Both ends authenticate |
Unauthorized access blocked |
6 |
Use TLS 1.3 |
Latest protocol used |
Strong encryption prevents MITM |
7 |
Use TLS 1.2 |
Secure protocol used |
MITM protection enabled |
8 |
Use OCSP Stapling |
Cert status verified |
Prevents forged certs |
9 |
Use HSTS |
Enforce HTTPS |
Prevents downgrade to HTTP |
10 |
Use Encrypted SNI |
Hide domain in handshake |
Prevents SNI-based MITM |
11 |
Use DNS over HTTPS |
Encrypt DNS queries |
Prevents DNS spoofing |
12 |
Use Secure Cookies |
Mark cookies as Secure |
Not sent over HTTP |
13 |
Use Secure Headers |
Use X-Content-Type-Options, etc. |
Prevents injection attacks |
14 |
Use HTTPS with API |
Secure API communication |
MITM blocked |
15 |
Use HTTPS with WebSocket |
Use wss:// |
Secure channel established |
16 |
Use HTTPS with CDN |
CDN uses valid cert |
End-to-end encryption |
17 |
Use HTTPS with Load Balancer |
TLS terminates securely |
MITM prevented at edge |
18 |
Use HTTPS with Reverse Proxy |
Proxy validates cert |
Secure routing |
19 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile App |
App validates cert |
Secure communication |
20 |
Use HTTPS with Desktop App |
App uses HTTPS |
Data protected |
21 |
Use HTTPS with IoT Device |
Device uses TLS |
Secure telemetry |
22 |
Use HTTPS with CLI Tool |
curl/wget validate cert |
MITM blocked |
23 |
Use HTTPS with SSO |
Secure login |
Identity protected |
24 |
Use HTTPS with OAuth |
Token exchange encrypted |
Tokens not intercepted |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Payment Gateway |
Submit payment securely |
Data not intercepted |
26 |
Use HTTPS with Email API |
Send email via HTTPS |
Content protected |
27 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Transparency |
Certs logged |
Forged certs detected |
28 |
Use HTTPS with CRL Check |
Check revocation list |
Revoked certs rejected |
29 |
Use HTTPS with Browser |
Browser validates cert |
MITM attempts blocked |
30 |
Use HTTPS with VPN |
HTTPS over VPN |
Double encryption |
31 |
Use HTTPS with Proxy |
Proxy validates cert |
Secure routing |
32 |
Use HTTPS with Firewall |
Inspect encrypted traffic |
MITM attempts detected |
33 |
Use HTTPS with Rate Limiting |
Secure enforcement |
No tampering |
34 |
Use HTTPS with Logging Tool |
Log secure traffic |
No data leakage |
35 |
Use HTTPS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor certs and ciphers |
MITM attempts flagged |
36 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Renewal |
Renew before expiry |
Continuous protection |
37 |
Use HTTPS with Certificate Rotation |
Rotate certs securely |
Prevent stale cert attacks |
38 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site |
Serve HTML securely |
Content not altered |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Dynamic Site |
Serve API securely |
Data not intercepted |
40 |
Use HTTPS with Analytics |
Send metrics securely |
Data not exposed |
41 |
Use HTTPS with Health Check |
Validate cert |
Secure status monitoring |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Port 443 |
Default secure port |
Encrypted communication |
43 |
Use HTTPS with Wildcard Cert |
Secure subdomains |
All protected |
44 |
Use HTTPS with SAN Cert |
Secure multiple domains |
All trusted |
45 |
Use HTTPS with SNI |
Cert selected by hostname |
Correct cert served |
46 |
Use HTTPS with CSP |
Prevent script injection |
Secure content |
47 |
Use HTTPS with Retry Logic |
Retry over secure channel |
No data leakage |
48 |
Use HTTPS with Compression |
Compress and encrypt |
Data integrity preserved |
49 |
Use HTTPS with File Upload |
Upload securely |
No interception |
50 |
Use HTTPS with File Download |
Download securely |
No tampering |
SEO and Browser Preference - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Access HTTPS Site in Chrome |
Open secure site |
Padlock icon shown |
2 |
Access HTTP Site in Chrome |
Open insecure site |
Not Secure warning shown |
3 |
Access HTTPS Site in Firefox |
Open secure site |
Padlock icon shown |
4 |
Access HTTP Site in Firefox |
Open insecure site |
Warning shown in address bar |
5 |
Access HTTPS Site in Edge |
Open secure site |
Secure indicator shown |
6 |
Access HTTP Site in Edge |
Open insecure site |
Not Secure label shown |
7 |
Access HTTPS Site in Safari |
Open secure site |
Padlock icon shown |
8 |
Access HTTP Site in Safari |
Open insecure site |
Warning shown |
9 |
Submit HTTPS Site to Google Search Console |
Add secure site |
Site indexed and ranked |
10 |
Submit HTTP Site to Google Search Console |
Add insecure site |
Lower ranking potential |
11 |
Compare SEO Ranking: HTTPS vs HTTP |
Same content, different protocol |
HTTPS ranks higher |
12 |
Use HTTPS with Sitemap |
Submit sitemap over HTTPS |
Google indexes securely |
13 |
Use HTTPS with Canonical Tags |
Canonical URL uses HTTPS |
Preferred version indexed |
14 |
Use HTTPS with Robots.txt |
File served over HTTPS |
Crawlers access securely |
15 |
Use HTTPS with Meta Tags |
Meta tags loaded securely |
SEO metadata trusted |
16 |
Use HTTPS with Structured Data |
JSON-LD over HTTPS |
Rich results eligible |
17 |
Use HTTPS with hreflang Tags |
Language tags over HTTPS |
International SEO supported |
18 |
Use HTTPS with AMP Pages |
AMP served over HTTPS |
Google caches and ranks |
19 |
Use HTTPS with Mobile-Friendly Test |
Test secure site |
Passes mobile SEO checks |
20 |
Use HTTPS with PageSpeed Insights |
Analyze secure site |
Higher performance score |
21 |
Use HTTPS with Core Web Vitals |
Measure secure site |
Metrics tracked accurately |
22 |
Use HTTPS with Google Analytics |
Track secure traffic |
Data collected securely |
23 |
Use HTTPS with Google Ads |
Run ads to HTTPS site |
Ads approved |
24 |
Use HTTPS with Facebook Sharing |
Share secure link |
Preview loads correctly |
25 |
Use HTTPS with Twitter Cards |
Share secure link |
Card preview shown |
26 |
Use HTTPS with LinkedIn Sharing |
Share secure link |
Metadata displayed |
27 |
Use HTTPS with Sitemap Ping |
Ping Google with HTTPS sitemap |
Sitemap accepted |
28 |
Use HTTPS with SSL Certificate |
Valid cert installed |
SEO boost applied |
29 |
Use HTTPS with HSTS |
Enforce HTTPS |
Google respects secure policy |
30 |
Use HTTPS with Redirect from HTTP |
301 redirect to HTTPS |
SEO value preserved |
31 |
Use HTTPS with Canonical Redirect |
Canonical points to HTTPS |
SEO authority consolidated |
32 |
Use HTTPS with Googlebot |
Googlebot crawls HTTPS |
Pages indexed |
33 |
Use HTTPS with Bingbot |
Bingbot crawls HTTPS |
Pages indexed |
34 |
Use HTTPS with Sitemap Index |
Multiple sitemaps over HTTPS |
All indexed |
35 |
Use HTTPS with Image Sitemap |
Images indexed securely |
SEO for images improved |
36 |
Use HTTPS with Video Sitemap |
Videos indexed securely |
Video SEO enhanced |
37 |
Use HTTPS with News Sitemap |
News content indexed |
Trusted by Google News |
38 |
Use HTTPS with SSL Labs Test |
Grade A rating |
SEO trust improved |
39 |
Use HTTPS with Google Lighthouse |
Audit secure site |
SEO score improved |
40 |
Use HTTPS with Google Discover |
Content eligible |
Secure content surfaced |
41 |
Use HTTPS with Google Shopping |
Product pages over HTTPS |
Listings approved |
42 |
Use HTTPS with Schema.org Markup |
Structured data over HTTPS |
Rich snippets shown |
43 |
Use HTTPS with Google Tag Manager |
Tags load securely |
No browser warnings |
44 |
Use HTTPS with Google Fonts |
Fonts loaded securely |
No mixed content |
45 |
Use HTTPS with CDN |
Assets served securely |
SEO and performance improved |
46 |
Use HTTPS with Static Site Generator |
Deploy secure site |
SEO-friendly |
47 |
Use HTTPS with WordPress |
Enable HTTPS |
SEO plugins work securely |
48 |
Use HTTPS with Shopify |
Store served over HTTPS |
SEO and trust improved |
49 |
Use HTTPS with Wix/Squarespace |
Enable HTTPS |
Site marked secure |
50 |
Use HTTPS with Google Safe Browsing |
Site passes checks |
No warnings shown |
Forward Secrecy - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Use TLS 1.3 |
Establish connection |
Forward secrecy enabled by default |
2 |
Use TLS 1.2 with ECDHE |
Use ephemeral Diffie-Hellman |
Forward secrecy achieved |
3 |
Use TLS 1.2 with DHE |
Use DHE cipher suite |
Session keys not reused |
4 |
Use RSA Key Exchange |
Use static RSA |
Forward secrecy not provided |
5 |
Use ECDHE-RSA Cipher |
Use ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 |
Forward secrecy enabled |
6 |
Use ECDHE-ECDSA Cipher |
Use ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 |
Forward secrecy enabled |
7 |
Use SSL Labs Test |
Scan site |
Forward secrecy supported shown |
8 |
Use Wireshark to Inspect Session |
Capture encrypted session |
Cannot decrypt without ephemeral key |
9 |
Compromise Server Private Key |
Try to decrypt past sessions |
Data remains secure |
10 |
Use TLS Session Resumption |
Resume session |
Forward secrecy preserved |
11 |
Use TLS with Session Tickets |
Resume with ticket |
Forward secrecy maintained if ticket encrypted |
12 |
Use TLS with Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) |
Enable PFS |
Past sessions protected |
13 |
Use TLS with Ephemeral Key Rotation |
Rotate keys per session |
No key reuse |
14 |
Use TLS with Key Logging Disabled |
No key logs |
Sessions cannot be decrypted |
15 |
Use TLS with Key Logging Enabled |
Log ephemeral keys |
Session can be decrypted (for debugging only) |
16 |
Use TLS with Weak Cipher |
Use RC4 or DES |
Forward secrecy not supported |
17 |
Use TLS with Strong Cipher |
Use AES-GCM with ECDHE |
Forward secrecy supported |
18 |
Use TLS with OpenSSL |
Configure ECDHE ciphers |
Forward secrecy enabled |
19 |
Use TLS with NGINX |
Enable ssl_prefer_server_ciphers |
Forward secrecy enforced |
20 |
Use TLS with Apache |
Configure SSLCipherSuite |
Forward secrecy enabled |
21 |
Use TLS with HAProxy |
Enable ephemeral ciphers |
Forward secrecy supported |
22 |
Use TLS with Cloudflare |
Enable PFS in dashboard |
Forward secrecy active |
23 |
Use TLS with AWS ELB |
Choose PFS-enabled policy |
Forward secrecy supported |
24 |
Use TLS with Azure Front Door |
Enable strong cipher suite |
Forward secrecy enabled |
25 |
Use TLS with Google Cloud Load Balancer |
Use modern TLS policy |
Forward secrecy supported |
26 |
Use TLS with CDN |
CDN supports ECDHE |
Forward secrecy preserved |
27 |
Use TLS with Mobile App |
App uses ECDHE |
Session keys not reused |
28 |
Use TLS with Desktop App |
App uses TLS 1.3 |
Forward secrecy by default |
29 |
Use TLS with IoT Device |
Device uses ephemeral keys |
Secure sessions |
30 |
Use TLS with WebSocket |
Use wss:// with ECDHE |
Forward secrecy maintained |
31 |
Use TLS with API Gateway |
Gateway supports PFS |
Secure API sessions |
32 |
Use TLS with Mutual TLS |
Both sides use ephemeral keys |
Forward secrecy preserved |
33 |
Use TLS with Certificate Pinning |
Cert pinned, ephemeral keys used |
Secure and trusted |
34 |
Use TLS with Monitoring Tool |
Monitor cipher usage |
PFS ciphers detected |
35 |
Use TLS with Logging Tool |
Log cipher suite |
Forward secrecy confirmed |
36 |
Use TLS with Security Scanner |
Scan for PFS support |
Report shows enabled |
37 |
Use TLS with Rate Limiting |
Secure sessions maintained |
No key reuse |
38 |
Use TLS with Session Timeout |
Expire sessions quickly |
Ephemeral keys discarded |
39 |
Use TLS with Key Rotation Policy |
Rotate certs and keys |
Forward secrecy unaffected |
40 |
Use TLS with Certificate Renewal |
Renew certs |
Past sessions remain secure |
41 |
Use TLS with Certificate Revocation |
Revoke cert |
Past sessions still protected |
42 |
Use TLS with Static DH |
Use DH without E |
Forward secrecy not supported |
43 |
Use TLS with ECDSA Certificate |
Use with ECDHE |
Forward secrecy enabled |
44 |
Use TLS with RSA Certificate |
Use with ECDHE |
Forward secrecy enabled |
45 |
Use TLS with Legacy Client |
Client does not support ECDHE |
Forward secrecy not available |
46 |
Use TLS with Modern Browser |
Browser supports ECDHE |
Forward secrecy enabled |
47 |
Use TLS with HTTP/2 |
Use ECDHE cipher |
Forward secrecy preserved |
48 |
Use TLS with HTTP/3 |
QUIC uses ephemeral keys |
Forward secrecy by design |
49 |
Use TLS with Cloud Gateway |
Gateway supports PFS |
Secure sessions |
50 |
Use TLS with Security Policy Audit |
Review cipher config |
Forward secrecy verified |
Compatiblity with HTTP - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Send GET Request via HTTPS |
Use GET method |
Server responds as with HTTP |
2 |
Send POST Request via HTTPS |
Use POST method |
Data submitted successfully |
3 |
Send PUT Request via HTTPS |
Use PUT method |
Resource updated |
4 |
Send DELETE Request via HTTPS |
Use DELETE method |
Resource deleted |
5 |
Send HEAD Request via HTTPS |
Use HEAD method |
Headers returned |
6 |
Send OPTIONS Request via HTTPS |
Use OPTIONS method |
Allowed methods listed |
7 |
Use Same URL Structure |
Use /api/data on HTTPS |
Server responds correctly |
8 |
Use Same Query Parameters |
Use ?id=123 |
Server processes query |
9 |
Use Same Headers |
Send Content-Type, Accept |
Server handles headers |
10 |
Use Same Status Codes |
Receive 200, 404, 500 |
Status codes consistent |
11 |
Use Same MIME Types |
Receive application/json, etc. |
Content types unchanged |
12 |
Use Same Cookies |
Send/receive cookies |
Cookies handled securely |
13 |
Use Same Redirects |
Use 301, 302 |
Redirects work over HTTPS |
14 |
Use Same Caching Headers |
Use Cache-Control, ETag |
Caching works as expected |
15 |
Use Same Content-Encoding |
Use gzip, br |
Compression supported |
16 |
Use Same Authentication Headers |
Use Authorization |
Auth works over HTTPS |
17 |
Use Same User-Agent |
Send browser info |
Server processes it |
18 |
Use Same Accept-Language |
Send language preference |
Server responds accordingly |
19 |
Use Same Content Negotiation |
Use Accept header |
Server returns correct format |
20 |
Use Same RESTful API |
Access /users/1 |
API responds over HTTPS |
21 |
Use Same Web Forms |
Submit form via HTTPS |
Server processes form |
22 |
Use Same File Upload |
Upload file via HTTPS |
File received |
23 |
Use Same File Download |
Download file via HTTPS |
File served correctly |
24 |
Use Same Static Assets |
Load CSS/JS/images |
Assets load securely |
25 |
Use Same JavaScript APIs |
Fetch data via fetch() |
Works over HTTPS |
26 |
Use Same HTML Forms |
Submit via HTTPS |
Form processed |
27 |
Use Same Redirect Logic |
Redirect from /old to /new |
Works over HTTPS |
28 |
Use Same Pagination |
Use ?page=2 |
Server returns correct page |
29 |
Use Same Filtering |
Use ?filter=active |
Server filters data |
30 |
Use Same Sorting |
Use ?sort=name |
Server sorts data |
31 |
Use Same Rate Limiting |
Apply limits per IP |
Limits enforced over HTTPS |
32 |
Use Same Error Handling |
Return 400, 403, 500 |
Errors handled the same |
33 |
Use Same Logging |
Log HTTPS requests |
Format unchanged |
34 |
Use Same Monitoring Tools |
Monitor HTTPS traffic |
Metrics collected |
35 |
Use Same Analytics Tools |
Track HTTPS traffic |
Data collected securely |
36 |
Use Same CDN |
Serve content over HTTPS |
CDN handles both protocols |
37 |
Use Same Load Balancer |
Route HTTP and HTTPS |
Load balanced correctly |
38 |
Use Same Reverse Proxy |
Proxy handles both |
Requests routed properly |
39 |
Use Same API Gateway |
Gateway supports both |
API accessible securely |
40 |
Use Same WebSocket Upgrade |
Upgrade to wss:// |
Connection established |
41 |
Use Same Mobile App Backend |
App switches to HTTPS |
No code changes needed |
42 |
Use Same Desktop App Backend |
App uses HTTPS |
Functionality preserved |
43 |
Use Same IoT Device Endpoint |
Device uses HTTPS |
Data transmitted securely |
44 |
Use Same CLI Tools |
curl/wget with HTTPS |
Commands unchanged |
45 |
Use Same Browser Behavior |
Load site via HTTPS |
UI and behavior consistent |
46 |
Use Same SEO Tags |
Meta tags work over HTTPS |
SEO unaffected |
47 |
Use Same Robots.txt |
File served over HTTPS |
Crawlers access it |
48 |
Use Same Sitemap |
Sitemap over HTTPS |
Search engines index it |
49 |
Use Same Canonical URLs |
Use HTTPS in canonical tag |
SEO preserved |
50 |
Use Same Analytics Scripts |
Load over HTTPS |
Tracking works securely |
Required for Modern Features - Testcases
# |
Test Case |
Description |
Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Enable HTTP/2 on HTTPS Site |
Use TLS with HTTP/2 |
Multiplexed streams supported |
2 |
Enable HTTP/3 on HTTPS Site |
Use QUIC protocol |
Faster, secure connection |
3 |
Register Service Worker |
Use navigator.serviceWorker.register() |
Registration succeeds only over HTTPS |
4 |
Install PWA |
Add to home screen |
Only allowed on HTTPS |
5 |
Use Push Notifications |
Request permission |
Works only on HTTPS |
6 |
Use Background Sync |
Sync data in background |
Requires HTTPS |
7 |
Use Web Bluetooth API |
Connect to device |
Requires secure context |
8 |
Use WebUSB API |
Access USB device |
HTTPS required |
9 |
Use WebRTC |
Establish peer connection |
Secure context required |
10 |
Use WebAuthn |
Authenticate with biometrics |
HTTPS required |
11 |
Use Geolocation API |
Request location |
Works only on HTTPS |
12 |
Use Clipboard API |
Read/write clipboard |
Requires HTTPS |
13 |
Use Payment Request API |
Initiate payment |
Secure context required |
14 |
Use Credential Management API |
Store credentials |
HTTPS required |
15 |
Use Device Orientation API |
Access motion sensors |
Secure context required |
16 |
Use Media Capture API |
Access camera/mic |
HTTPS required |
17 |
Use Web Share API |
Share content |
Secure context required |
18 |
Use Web NFC |
Read/write NFC tags |
HTTPS required |
19 |
Use WebXR |
Access AR/VR features |
Secure context required |
20 |
Use Web Speech API |
Speech recognition |
HTTPS required for full support |
21 |
Use WebAssembly |
Load .wasm modules |
Secure context preferred |
22 |
Use IndexedDB |
Store data offline |
Works better with HTTPS |
23 |
Use Cache API |
Cache assets for offline use |
Requires HTTPS |
24 |
Use Fetch API |
Make secure requests |
HTTPS ensures integrity |
25 |
Use Notification API |
Show browser notifications |
HTTPS required |
26 |
Use Manifest.json |
Define PWA metadata |
Must be served over HTTPS |
27 |
Use App Install Banner |
Trigger install prompt |
Requires HTTPS |
28 |
Use Lazy Loading |
Load images on scroll |
Works best with HTTPS |
29 |
Use Content Security Policy |
Enforce CSP |
Secure delivery required |
30 |
Use Subresource Integrity |
Verify asset hashes |
HTTPS ensures trust |
31 |
Use Secure Cookies |
Mark cookies as Secure |
Only sent over HTTPS |
32 |
Use SameSite Cookies |
Enhance cookie security |
HTTPS improves enforcement |
33 |
Use HSTS |
Enforce HTTPS |
Required for modern security |
34 |
Use HTTP/2 Server Push |
Push assets to client |
Requires HTTPS |
35 |
Use Brotli Compression |
Serve compressed assets |
Supported over HTTPS |
36 |
Use WebSockets Securely |
Use wss:// |
Secure connection established |
37 |
Use WebGL |
Render 3D graphics |
Secure context preferred |
38 |
Use AudioContext |
Process audio |
Secure context required for full features |
39 |
Use Web Workers |
Run scripts in background |
HTTPS ensures isolation |
40 |
Use Shared Workers |
Share data between tabs |
Secure context required |
41 |
Use Cross-Origin Isolation |
Enable COOP/COEP |
HTTPS required |
42 |
Use Feature Policy |
Restrict APIs |
Enforced over HTTPS |
43 |
Use Permissions Policy |
Control feature access |
Requires secure context |
44 |
Use Secure DNS (DoH) |
Resolve DNS over HTTPS |
Prevents spoofing |
45 |
Use WebSockets with HTTP/2 |
Use wss:// with multiplexing |
Secure and efficient |
46 |
Use WebTransport |
Low-latency transport |
Requires HTTPS |
47 |
Use WebCodecs |
Stream media efficiently |
Secure context required |
48 |
Use WebGPU |
Access GPU for rendering |
HTTPS required |
49 |
Use Federated Credential Management |
Login with federated identity |
HTTPS required |
50 |
Use Secure Context Check |
window.isSecureContext |
Returns true on HTTPS |
Reference links