Basic example icmp server and client
In this program, you are going to learn
How to create a Socket ?
How to send a data ?
How to recv a data ?
Topics in this section,
Topics in this section,
Let us answer few basic questions in this socket
What does socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP) do?
See Answer
This call creates a raw socket in the IPv4 address family (AF_INET) that can
receive ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets directly.
Why use AF_INET as the address family?
See Answer
AF_INET specifies that the socket will work with IPv4 addresses.
What is the purpose of SOCK_RAW in the socket type?
See Answer
SOCK_RAW allows the socket to operate at a lower level by providing direct access to the packet,
including the IP and transport layer headers.
Why specify IPPROTO_ICMP as the protocol?
See Answer
It filters the socket to receive only ICMP packets, allowing applications to handle ICMP messages directly.
Can this socket send ICMP packets as well?
See Answer
Yes, the same socket can be used to send and receive ICMP packets.
How does this socket differ from a standard UDP or TCP socket?
See Answer
Unlike UDP or TCP sockets, a raw socket provides direct access to the IP and ICMP headers, making it suitable for low-level packet handling.
Is error checking needed after creating the socket?
See Answer
Yes, checking for errors ensures that the socket is created successfully before proceeding with further operations.
Can this socket be used for other protocols besides ICMP?
See Answer
While created specifically for ICMP, the socket can be adapted for handling other IP protocols by changing the IPPROTO parameter.
Why close the socket after processing?
See Answer
Closing the socket ensures proper resource cleanup and releases the associated system resources.
How is the source IP address extracted from the received packet?
See Answer
The source IP address can be extracted by parsing the IP header within the received packet.
Can this socket receive ICMP messages from any source?
See Answer
Yes, the socket can receive ICMP packets from any source as it operates at the network layer.
Why cast to struct iphdr and struct icmphdr in packet processing?
See Answer
Casting allows the code to interpret the received buffer as IP and ICMP headers, facilitating packet analysis.
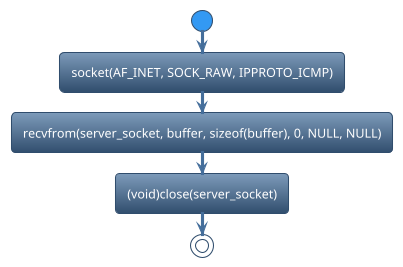
There are many functions used in socket. We can classify those functions based on functionalities.
Create Socket
Recv data_packet
Close socket
socket()is used to create a new socket. For example,
server_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
recvfromis used in network programming to receive data from a connected socket. For example,
ret = recvfrom(server_socket, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
closeis used to close the socket To free up system resources associated with the socket. For example,
(void)close(server_socket);
See the full program below,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
int server_socket = -1;
static void sigint_handler(int signo)
{
(void)close(server_socket);
sleep(2);
(void)printf("Caught sigINT!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void register_signal_handler(
int signum,
void (*handler)(int))
{
if (signal(signum, handler) ==
SIG_ERR) {
printf("Cannot handle signal\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
int main()
{
int ret;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *original_data;
struct iphdr *ip_header;
struct icmphdr *icmp_header;
register_signal_handler(SIGINT,
sigint_handler);
server_socket = socket(AF_INET,
SOCK_RAW,
IPPROTO_ICMP);
if (server_socket < 0) {
perror("Socket failed");
return -1;
}
ret = recvfrom(server_socket,
buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("recv");
(void)close(server_socket);
return -2;
}
ip_header = (struct iphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header = (struct icmphdr *)
(buffer + sizeof(struct iphdr));
original_data = buffer +
sizeof(struct iphdr) +
sizeof(struct icmphdr);
printf("Received ICMP message\n");
printf("Source IP: %s\n",
inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)&
(ip_header->saddr)));
printf("Type: %d\n",
icmp_header->type);
printf("Code: %d\n",
icmp_header->code);
printf("Original Data: %s\n",
original_data);
printf("added ip header\n");
printf("recvied icmp hex dump\n");
for (int i = 0; i < ret; i++) {
printf("%02X ",
(unsigned char)buffer[i]);
}
(void)close(server_socket);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o server server.c
$ sudo ./server
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E F1 2A 40 00 40 01 4B A2 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
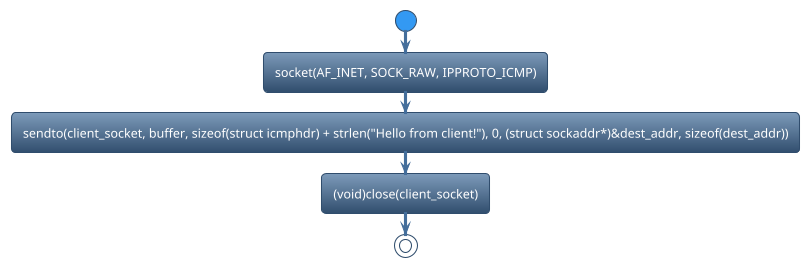
There are many functions used in socket. We can classify those functions based on functionalities.
Create Socket
Sendto data_packet
Close socket
socketis used to create a new socket. For example,
client_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
sendtois used to send the encoded message to the specified server address and port using a socket. For example,
ret = sendto(client_socket, buffer, sizeof(struct icmphdr) + strlen("Hello from client!"), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&dest_addr, sizeof(dest_addr));
closeis used to close the socket To free up system resources associated with the socket. For example,
(void)close(client_socket);
See the full program below,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
int client_socket = -1;
static void sigint_handler(
int signo)
{
(void)close(client_socket);
sleep(2);
(void)printf("Caught sigINT!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void register_signal_handler(
int signum,
void (*handler)(int))
{
if (signal(signum, handler) ==
SIG_ERR) {
printf("Cannot handle signal\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void validate_convert_addr(
char *ip_str,
struct sockaddr_in *sock_addr)
{
if (ip_str == NULL) {
perror("Invalid ip_str\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (sock_addr == NULL) {
perror("Invalid sock_addr\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("IP Address: %s\n", ip_str);
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, ip_str,
&(sock_addr->sin_addr)) <= 0) {
perror("Invalid address\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
struct sockaddr_in
dest_addr;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
struct icmphdr *icmp_header;
register_signal_handler(SIGINT,
sigint_handler);
if (argc != 2) {
printf("%s<ip-addr>\n",
argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
client_socket = socket(AF_INET,
SOCK_RAW,
IPPROTO_ICMP);
if (client_socket < 0) {
perror("Socket failed");
return -1;
}
memset(&dest_addr, 0,
sizeof(dest_addr));
dest_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
validate_convert_addr(argv[1],
&dest_addr);
snprintf(buffer +
sizeof(struct icmphdr),
sizeof(buffer) -
sizeof(struct icmphdr),
"Hello from client!");
icmp_header =
(struct icmphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header->type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp_header->code = 0;
icmp_header->checksum = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.id = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.sequence = 0;
ret = sendto(client_socket, buffer,
sizeof(struct icmphdr) +
strlen("Hello from client!"), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&dest_addr,
sizeof(dest_addr));
if (ret < 0) {
perror("sendto");
(void)close(client_socket);
return -2;
}
printf("sending icmp hex dump\n");
for (int i = 0; i < ret; i++) {
printf("%02X ",
(unsigned char)buffer[i]);
}
(void)close(client_socket);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o client client.c
$ sudo ./client 127.0.0.1
IP Address: 127.0.0.1
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
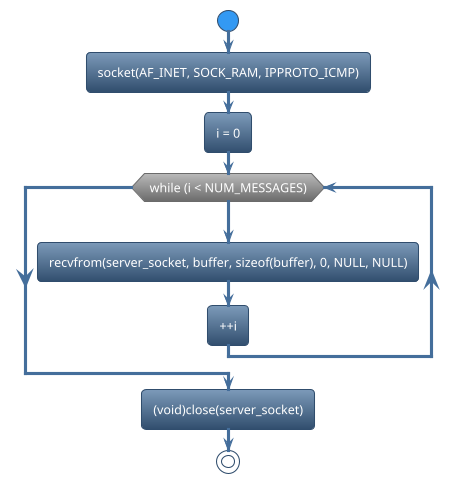
There are many functions used in socket. We can classify those functions based on functionalities.
Create Socket
Recv data_packet
Close socket
socket()is used to create a new socket. For example,
server_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
recvfromis used in network programming to receive data from a connected socket. For example,
ret = recvfrom(server_socket, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
closeis used to close the socket To free up system resources associated with the socket. For example,
(void)close(server_socket);
See the full program below,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
#define NUM_MESSAGES 10
int server_socket = -1;
static void sigint_handler(
int signo)
{
(void)close(server_socket);
sleep(2);
(void)printf("Caught sigINT!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void register_signal_handler(
int signum,
void (*handler)(int))
{
if (signal(signum, handler) ==
SIG_ERR) {
printf("Cannot handle signal\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
int main()
{
int ret, i;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *original_data;
struct iphdr *ip_header;
struct icmphdr *icmp_header;
register_signal_handler(SIGINT,
sigint_handler);
server_socket = socket(AF_INET,
SOCK_RAW,
IPPROTO_ICMP);
if (server_socket < 0) {
perror("Socket failed");
return -1;
}
i = 0;
while (i < NUM_MESSAGES) {
ret = recvfrom(server_socket,
buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("recv");
(void)close(server_socket);
return -2;
}
ip_header =
(struct iphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header =
(struct icmphdr *)
(buffer +
sizeof(struct iphdr));
original_data = buffer +
sizeof(struct iphdr) +
sizeof(struct icmphdr);
printf("Received ICMP message\n");
printf("Source IP: %s\n",
inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)&
(ip_header->saddr)));
printf("Type: %d\n",
icmp_header->type);
printf("Code: %d\n",
icmp_header->code);
printf("Original Data: %s\n",
original_data);
printf("\n\n Recevied %d time\n",
i);
printf("added ip header\n");
printf("recvied icmp hex dump\n");
for (int i = 0; i < ret; i++) {
printf("%02X ",
(unsigned char)buffer[i]);
}
++i;
}
(void)close(server_socket);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o server server.c
$ sudo ./server
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 0 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 36 40 00 40 01 C4 96 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 1 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 37 40 00 40 01 C4 95 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 2 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 38 40 00 40 01 C4 94 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 3 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 39 40 00 40 01 C4 93 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 4 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 3A 40 00 40 01 C4 92 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 5 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 3B 40 00 40 01 C4 91 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 6 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 3C 40 00 40 01 C4 90 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 7 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 3D 40 00 40 01 C4 8F 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 8 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 3E 40 00 40 01 C4 8E 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Received ICMP message
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Recevied 9 time
added ip header
recvied icmp hex dump
45 00 00 2E 78 3F 40 00 40 01 C4 8D 7F 00 00 01 7F 00 00 01 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
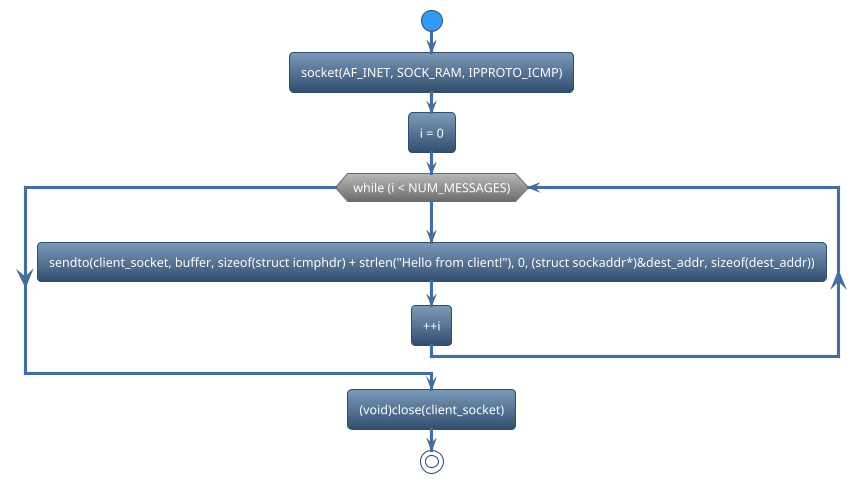
There are many functions used in socket. We can classify those functions based on functionalities.
Create Socket
Sendto data_packet
Close socket
socketis used to create a new socket. For example,
client_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
sendtois used to send the encoded message to the specified server address and port using a socket. For example,
ret = sendto(client_socket, buffer, sizeof(struct icmphdr) + strlen("Hello from client!"), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&dest_addr, sizeof(dest_addr));
closeis used to close the socket To free up system resources associated with the socket. For example,
(void)close(client_socket);
See the full program below,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
#define NUM_MESSAGES 10
int client_socket = -1;
static void sigint_handler(int signo)
{
(void)close(client_socket);
sleep(2);
(void)printf("Caught sigINT!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void register_signal_handler(
int signum,
void (*handler)(int))
{
if (signal(signum, handler) ==
SIG_ERR) {
printf("Cannot handle signal\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void validate_convert_addr(
char *ip_str,
struct sockaddr_in *sock_addr)
{
if (ip_str == NULL) {
perror("Invalid ip_str\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (sock_addr == NULL) {
perror("Invalid sock_addr\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("IP Address: %s\n", ip_str);
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, ip_str,
&(sock_addr->sin_addr)) <= 0) {
perror("Invalid address\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret, i;
struct sockaddr_in
dest_addr;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
struct icmphdr *icmp_header;
register_signal_handler(SIGINT,
sigint_handler);
if (argc != 2) {
printf("%s<ip-addr>\n",
argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
client_socket = socket(AF_INET,
SOCK_RAW,
IPPROTO_ICMP);
if (client_socket < 0) {
perror("Socket failed");
return -1;
}
memset(&dest_addr, 0,
sizeof(dest_addr));
dest_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
validate_convert_addr(argv[1],
&dest_addr);
snprintf(buffer +
sizeof(struct icmphdr),
sizeof(buffer) - sizeof(struct icmphdr),
"Hello from client!");
icmp_header =
(struct icmphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header->type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp_header->code = 0;
icmp_header->checksum = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.id = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.sequence = 0;
i = 0;
while (i < NUM_MESSAGES) {
ret = sendto(client_socket, buffer,
sizeof(struct icmphdr) +
strlen("Hello from client!"), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&dest_addr,
sizeof(dest_addr));
if (ret < 0) {
perror("sendto");
(void)close(client_socket);
return -2;
}
printf("sending icmp hex dump\n");
for (int i = 0; i < ret; i++) {
printf("%02X ",
(unsigned char)buffer[i]);
}
printf("\n\n Sent %d time\n",
i);
++i;
}
(void)close(client_socket);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o client client.c
$ sudo ./client 8080 127.0.0.1
IP Address: 127.0.0.1
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 0 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 1 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 2 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 3 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 4 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 5 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 6 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 7 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 8 time
sending icmp hex dump
08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 48 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 72 6F 6D 20 63 6C 69 65 6E 74 21
Sent 9 time
Default Domain:
By default, the socket is configured to work in the
AF_INETdomain, handling all types of network data.
Additional Domain Support:
We expand the socket’s capabilities to also function in the
PF_INETdomain, allowing it to operate similarly toAF_INET.
Socket Creation:
We set up a network connection point known as a socket using
socket(PF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP).
Working Scenario:
Despite the change in domain to
PF_INET, the socket continues to operate the same way, handling general network data.
Socket API |
Learning |
|---|---|
socket |
Create a new socket |
recvfrom |
It provides information about the source (sender) of the data, including the sender’s IP address and port number. |
sendto |
Send the encoded message to the specified server address and port using a socket. |
Previous topic
Current topic
Next topic
Other sockets
Other IPCs