IPV4 RAW AF INET ICMP server client program with Select system call
In this program, you are going to learn
How to create a Socket ?
How to send a data ?
How to recv a data ?
Let us answer few basic questions in this socket
What does socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP) do?
See Answer
This call creates a raw socket in the IPv4 address family (AF_INET) that can
receive ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets directly.
Why use AF_INET as the address family?
See Answer
AF_INET specifies that the socket will work with IPv4 addresses.
What is the purpose of SOCK_RAW in the socket type?
See Answer
SOCK_RAW allows the socket to operate at a lower level by providing direct access to the packet,
including the IP and transport layer headers.
Why specify IPPROTO_ICMP as the protocol?
See Answer
It filters the socket to receive only ICMP packets, allowing applications to handle ICMP messages directly.
Can this socket send ICMP packets as well?
See Answer
Yes, the same socket can be used to send and receive ICMP packets.
How does this socket differ from a standard UDP or TCP socket?
See Answer
Unlike UDP or TCP sockets, a raw socket provides direct access to the IP and ICMP headers, making it suitable for low-level packet handling.
Is error checking needed after creating the socket?
See Answer
Yes, checking for errors ensures that the socket is created successfully before proceeding with further operations.
Can this socket be used for other protocols besides ICMP?
See Answer
While created specifically for ICMP, the socket can be adapted for handling other IP protocols by changing the IPPROTO parameter.
Why close the socket after processing?
See Answer
Closing the socket ensures proper resource cleanup and releases the associated system resources.
How is the source IP address extracted from the received packet?
See Answer
The source IP address can be extracted by parsing the IP header within the received packet.
Can this socket receive ICMP messages from any source?
See Answer
Yes, the socket can receive ICMP packets from any source as it operates at the network layer.
Why cast to struct iphdr and struct icmphdr in packet processing?
See Answer
Casting allows the code to interpret the received buffer as IP and ICMP headers, facilitating packet analysis.
What is the purpose of the select system call in network programming?
See Answer
To block and wait for activity on one or more file descriptors.
How does select help in handling multiple sockets efficiently?
See Answer
It provides a way to wait for readiness on multiple sockets without blocking the entire program.
What types of file descriptors can be monitored using select?
See Answer
sockets, files, timerfd, socketpair, message_queue, Namedpipes and shared_memory.
What is the significance of the timeout parameter in the select function?
See Answer
It specifies the maximum duration to wait for any file descriptor to become ready.
How do you handle errors when using the select system call?
See Answer
Check the return value for -1 to detect errors, Use perror to print error messages.
How does select handle a set of file descriptors with different states (e.g., reading, writing, exception)?
See Answer
- Preparing File Descriptor Sets:
select(readfds, writefds, exceptfds);- Setting Up Readiness Conditions:
If you are interested in monitoring file descriptors for readability, you add them to the readfds set.
FD_ZERO(&readfds);FD_SET(fd1, &readfds);- Setting Up Writability Conditions:
If you are interested in monitoring file descriptors for writability, you add them to the writefds set.
FD_ZERO(&writefds);FD_SET(fd2, &writefds);- Setting Up Exceptional Conditions:
If you are interested in monitoring file descriptors for exceptional conditions, you add them to the exceptfds set.
FD_ZERO(&exceptfds);FD_SET(fd3, &exceptfds);
How does select Checking Ready File Descriptors?
See Answer
After select returns, you can check the sets to determine which file descriptors are ready for the specified conditions.
if (FD_ISSET(fd1, &readfds)) {
// fd1 is ready for reading
}
if (FD_ISSET(fd3, &writefds)) {
// fd2 is ready for writing
}
if (FD_ISSET(fd4, &exceptfds)) {
// fd3 has an exceptional condition
}
What does it mean if select returns 0?
See Answer
No file descriptors are ready within the specified timeout.
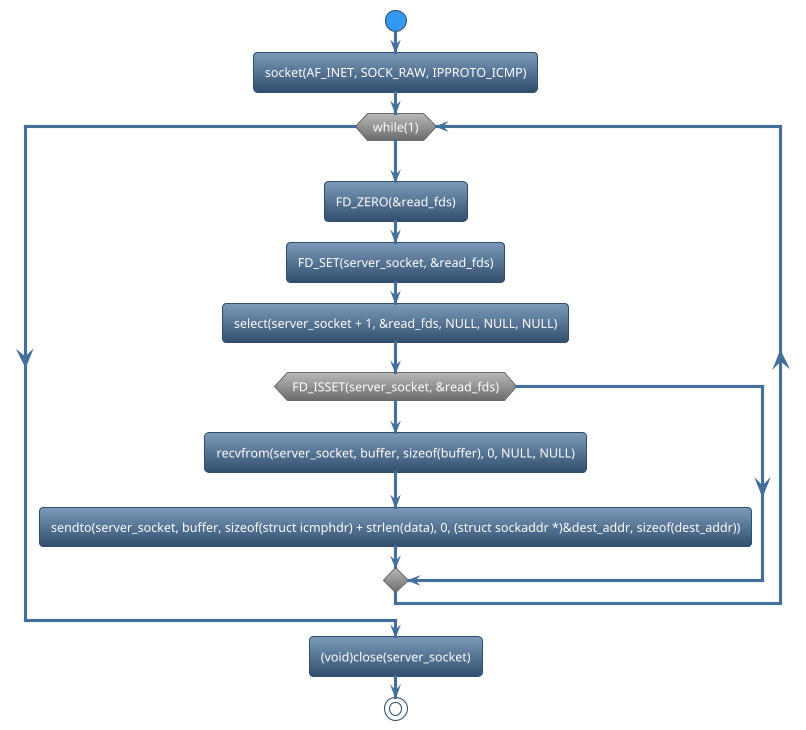
There are many functions used in socket. We can classify those functions based on functionalities.
Create Socket
Select
Recvfrom data_packet
Sendto data_packet
Close socket
socket()is used to create a new socket. For example,
server_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
select()is used in network programming to monitor multiple file descriptors (usually sockets) for read, write, or error conditions. For example,
ret = select(server_socket + 1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
recvfromis commonly used with sockets, where communication is connectionless. it provides information about the source (sender) of the data, including the sender’s IP address and port number. For example,
len = recvfrom(server_socket, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
sendtois used to send the encoded message to the specified server address and port using a socket. For example,
ret = sendto(server_socket, buffer, sizeof(struct icmphdr) + strlen(data), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&dest_addr, sizeof(dest_addr));
closeis used to close the socket To free up system resources associated with the socket. For example,
(void)close(server_socket);
See the full program below,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
int server_socket = -1;
static void sigint_handler(int signo)
{
(void)close(server_socket);
sleep(2);
(void)printf("Caught sigINT!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void register_signal_handler(
int signum,
void (*handler)(int))
{
if (signal(signum, handler) ==
SIG_ERR) {
printf("Cannot handle signal\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void send_icmp_message(
int client_socket,
const char *data)
{
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
struct sockaddr_in
dest_addr;
int ret;
struct icmphdr
*icmp_header;
snprintf(buffer +
sizeof(struct icmphdr),
sizeof(buffer) -
sizeof(struct icmphdr), "%s",
data);
icmp_header =
(struct icmphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header->type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp_header->code = 0;
icmp_header->checksum = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.id = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.sequence = 0;
ret = sendto(client_socket,
buffer, sizeof(struct icmphdr) +
strlen(data), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&dest_addr,
sizeof(dest_addr));
if (ret < 0) {
perror("sendto");
(void)close(client_socket);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void process_icmp_message(
char *buffer,
ssize_t length)
{
struct iphdr
*ip_header;
struct icmphdr
*icmp_header;
char *original_data;
icmp_header = (struct icmphdr *)
(buffer + sizeof(struct iphdr));
ip_header = (struct iphdr *)buffer;
printf("Received ICMP message:\n");
printf("Source IP: %s\n",
inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)&
(ip_header->saddr)));
printf("Type: %d\n", icmp_header->type);
printf("Code: %d\n", icmp_header->code);
original_data = buffer +
sizeof(struct iphdr) +
sizeof(struct icmphdr);
printf("Original Data: %s\n",
original_data);
}
int main()
{
int ret;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
fd_set read_fds;
register_signal_handler(SIGINT,
sigint_handler);
server_socket = socket(AF_INET,
SOCK_RAW,
IPPROTO_ICMP);
if (server_socket < 0) {
perror("Socket failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fcntl(server_socket,
F_SETFL,
O_NONBLOCK);
FD_ZERO(&read_fds);
FD_SET(server_socket, &read_fds);
while (1) {
FD_SET(server_socket, &read_fds);
ret = select(server_socket + 1,
&read_fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("select");
break;
}
if (FD_ISSET(server_socket, &read_fds)) {
ret = recvfrom(server_socket,
buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("recv");
break;
}
process_icmp_message(buffer, ret);
send_icmp_message(server_socket,
"Hello from server!");
sleep(2);
}
}
(void)close(server_socket);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o server server.c
$ sudo ./server
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from server!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from server!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from server!
^CCaught sigINT!
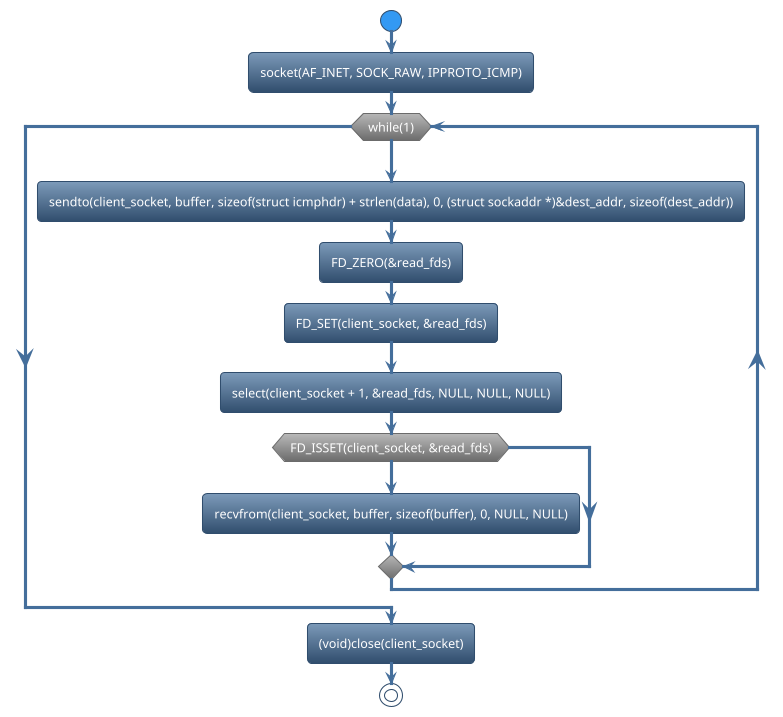
There are many functions used in socket. We can classify those functions based on functionalities.
Create Socket
Select
Sendto data_packet
Recvfrom data_packet
Close socket
socketis used to create a new socket. For example,
client_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
selectis used in network programming to monitor multiple file descriptors (usually sockets) for read, write, or error conditions. For example,
ret = select(client_socket + 1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
recvfromis commonly used with sockets, where communication is connectionless. it provides information about the source (sender) of the data, including the sender’s IP address and port number. For example,
len = recvfrom(client_socket, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
sendtois used to send the encoded message to the specified server address and port using a socket. For example,
ret = sendto(client_socket, buffer, sizeof(struct icmphdr) + strlen(data), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&dest_addr, sizeof(dest_addr));
closeis used to close the socket To free up system resources associated with the socket. For example,
(void)close(client_socket);
See the full program below,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
struct sockaddr_in
dest_addr;
int client_socket = -1;
static void sigint_handler(int signo)
{
(void)close(client_socket);
sleep(2);
(void)printf("Caught sigINT!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void register_signal_handler(
int signum,
void (*handler)(int))
{
if (signal(signum, handler) ==
SIG_ERR) {
printf("Cannot handle signal\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void validate_convert_addr(
char *ip_str,
struct sockaddr_in *sock_addr)
{
if (ip_str == NULL) {
perror("Invalid ip_str\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (sock_addr == NULL) {
perror("Invalid sock_addr\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("IP Address: %s\n", ip_str);
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, ip_str,
&(sock_addr->sin_addr)) <= 0) {
perror("Invalid address\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void send_icmp_message(
int client_socket,
const char *data)
{
int ret;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
struct icmphdr *icmp_header;
snprintf(buffer +
sizeof(struct icmphdr), sizeof(buffer) -
sizeof(struct icmphdr), "%s", data);
icmp_header = (struct icmphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header->type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp_header->code = 0;
icmp_header->checksum = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.id = 0;
icmp_header->un.echo.sequence = 0;
ret = sendto(client_socket,
buffer, sizeof(struct icmphdr) +
strlen(data), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&dest_addr,
sizeof(dest_addr));
if (ret < 0) {
perror("sendto");
(void)close(client_socket);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void process_icmp_message(
char *buffer,
ssize_t length)
{
struct iphdr *ip_header;
struct icmphdr *icmp_header;
char *original_data;
ip_header = (struct iphdr *)buffer;
icmp_header = (struct icmphdr *)
(buffer + sizeof(struct iphdr));
printf("Received ICMP message:\n");
printf("Source IP: %s\n",
inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)&
(ip_header->saddr)));
printf("Type: %d\n", icmp_header->type);
printf("Code: %d\n", icmp_header->code);
original_data = buffer +
sizeof(struct iphdr) +
sizeof(struct icmphdr);
printf("Original Data: %s\n",
original_data);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
fd_set read_fds;
register_signal_handler(SIGINT,
sigint_handler);
if (argc != 2) {
printf("%s <ip-addr>",
argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
memset(&dest_addr, 0,
sizeof(dest_addr));
dest_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
validate_convert_addr(argv[1],
&dest_addr);
client_socket = socket(AF_INET,
SOCK_RAW,
IPPROTO_ICMP);
if (client_socket < 0) {
perror("Socket failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fcntl(client_socket,
F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
while (1) {
send_icmp_message(client_socket,
"Hello from client!");
sleep(2);
FD_ZERO(&read_fds);
FD_SET(client_socket, &read_fds);
ret = select(client_socket + 1,
&read_fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("select");
break;
}
if (FD_ISSET(client_socket, &read_fds)) {
ret = recvfrom(client_socket,
buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("recv");
break;
} else {
process_icmp_message(buffer, ret);
}
}
}
(void)close(client_socket);
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o client client.c
$ sudo ./client 127.0.0.1
IP Address: 127.0.0.1
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from server!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from server!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from client!
Received ICMP message:
Source IP: 127.0.0.1
Type: 8
Code: 0
Original Data: Hello from server!
Default Domain:
By default, the socket is configured to work in the
AF_INETdomain, handling all types of network data.
Additional Domain Support:
We expand the socket’s capabilities to also function in the
PF_INETdomain, allowing it to operate similarly toAF_INET.
Socket Creation:
We set up a network connection point known as a socket using
socket(PF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP).
Working Scenario:
Despite the change in domain to
PF_INET, the socket continues to operate the same way, handling general network data.
Socket API |
Learning |
|---|---|
socket |
Create a new socket |
select |
Monitor multiple file descriptors (usually sockets) for read, write, or error conditions. |
recvfrom |
It provides information about the source (sender) of the data, including the sender’s IP address and port number. |
sendto |
Send the encoded message to the specified server address and port using a socket. |
Previous topic
Current topic
Next topic
Other sockets
Other IPCs